Ammonia, an essential compound used in fertilizers, plays a crucial role in agriculture and various industries. With the increasing focus on sustainable practices, researchers at the RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science (CSRS) in Japan have made a groundbreaking discovery. Led by Satoshi Kamiguchi, the team has developed a new catalyst that offers a greener and more energy-efficient method for producing ammonia.
Ammonia is not only vital for enhancing crop yields through fertilizers but also serves as a safe hydrogen storage medium and an alternative source of fuel. The traditional method of synthesizing ammonia, known as the Haber-Bosch process, involves high pressure and temperature conditions, resulting in significant energy consumption. The widespread use of ammonia in various industries further exacerbates its energy footprint, making it imperative to find more sustainable production methods.
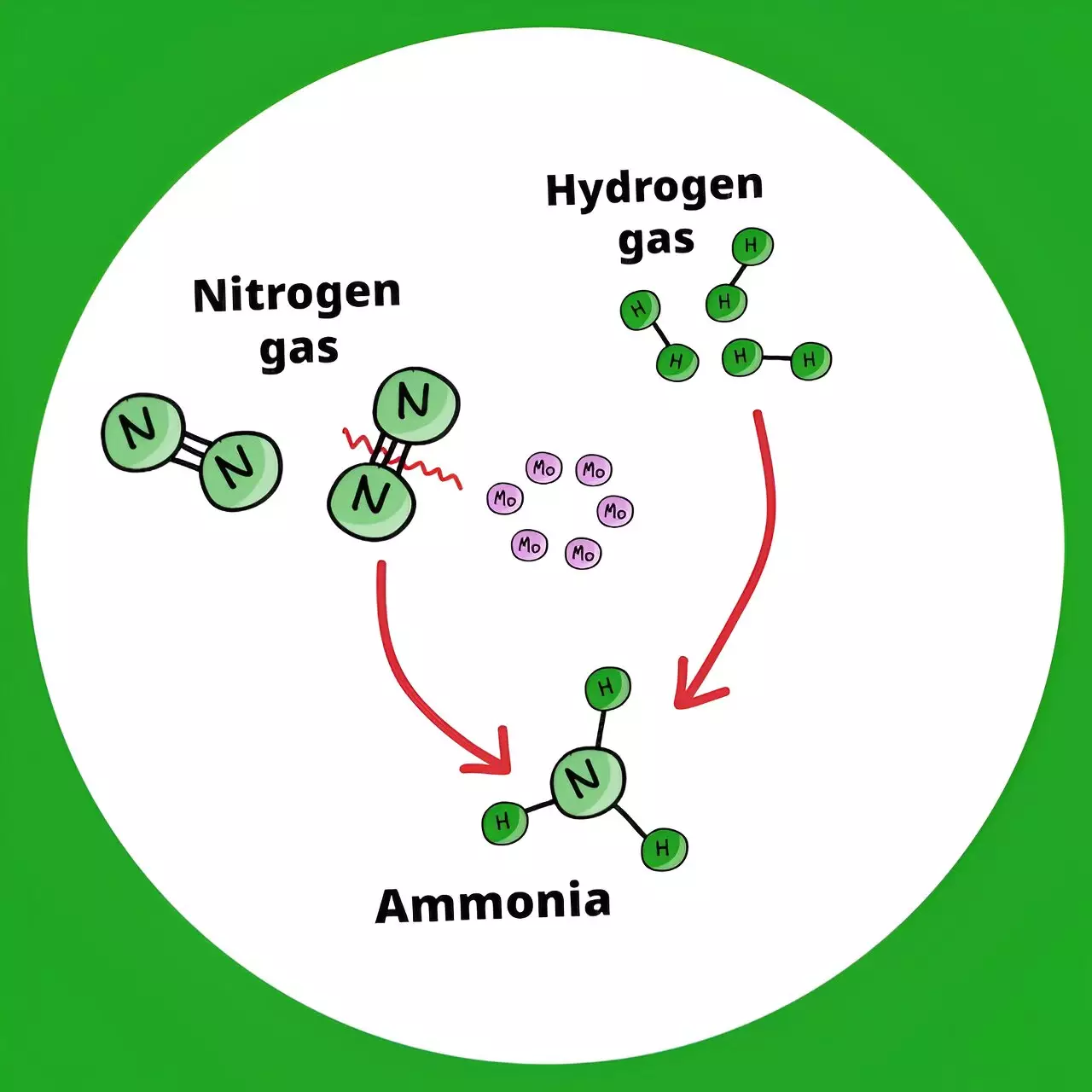
The key breakthrough in the research conducted by the RIKEN CSRS team lies in the development of a novel catalyst that enables the stable production of ammonia at lower temperatures. By utilizing ultrasmall molybdenum metal particles activated with hydrogen gas, the catalyst effectively breaks down the strong nitrogen-nitrogen bonds, facilitating ammonia synthesis. This innovative approach not only reduces the energy required for the process but also extends the longevity of the catalyst, allowing for continuous production of ammonia.
The potential impact of this new catalyst extends far beyond the realm of fertilizers. The ability to produce ammonia at lower energy costs opens the door to widespread adoption of ammonia fuel, which emits no CO2 when burned. By replacing the energy-intensive Haber-Bosch process with the more efficient catalyst developed by the RIKEN CSRS team, significant reductions in carbon emissions can be achieved. Moreover, the use of ammonia as a carrier for hydrogen presents a promising avenue for sustainable energy storage and utilization.
While the new catalyst offers a promising path towards greener ammonia production, challenges remain. The current reliance on fossil fuels for hydrogen production poses a significant obstacle to achieving carbon neutrality. However, by integrating the catalyst system with green hydrogen production methods using renewable energy sources, the emission of global-warming CO2 can be further minimized. The ongoing research efforts to enhance the efficiency of ammonia synthesis through the addition of promoters underscore the commitment of the RIKEN CSRS team to advancing sustainable solutions.
The discovery of a new catalyst for ammonia production represents a significant step towards a more sustainable and energy-efficient future. By revolutionizing the way ammonia is synthesized, researchers are paving the way for a greener economy and reduced carbon emissions. The potential of ammonia as a key player in the transition to renewable energy sources highlights the importance of continued innovation in the field of catalysis and sustainable resource management. As we strive towards a greener future, initiatives like the one undertaken by the RIKEN CSRS team offer hope for a more environmentally conscious and sustainable world.


Leave a Reply