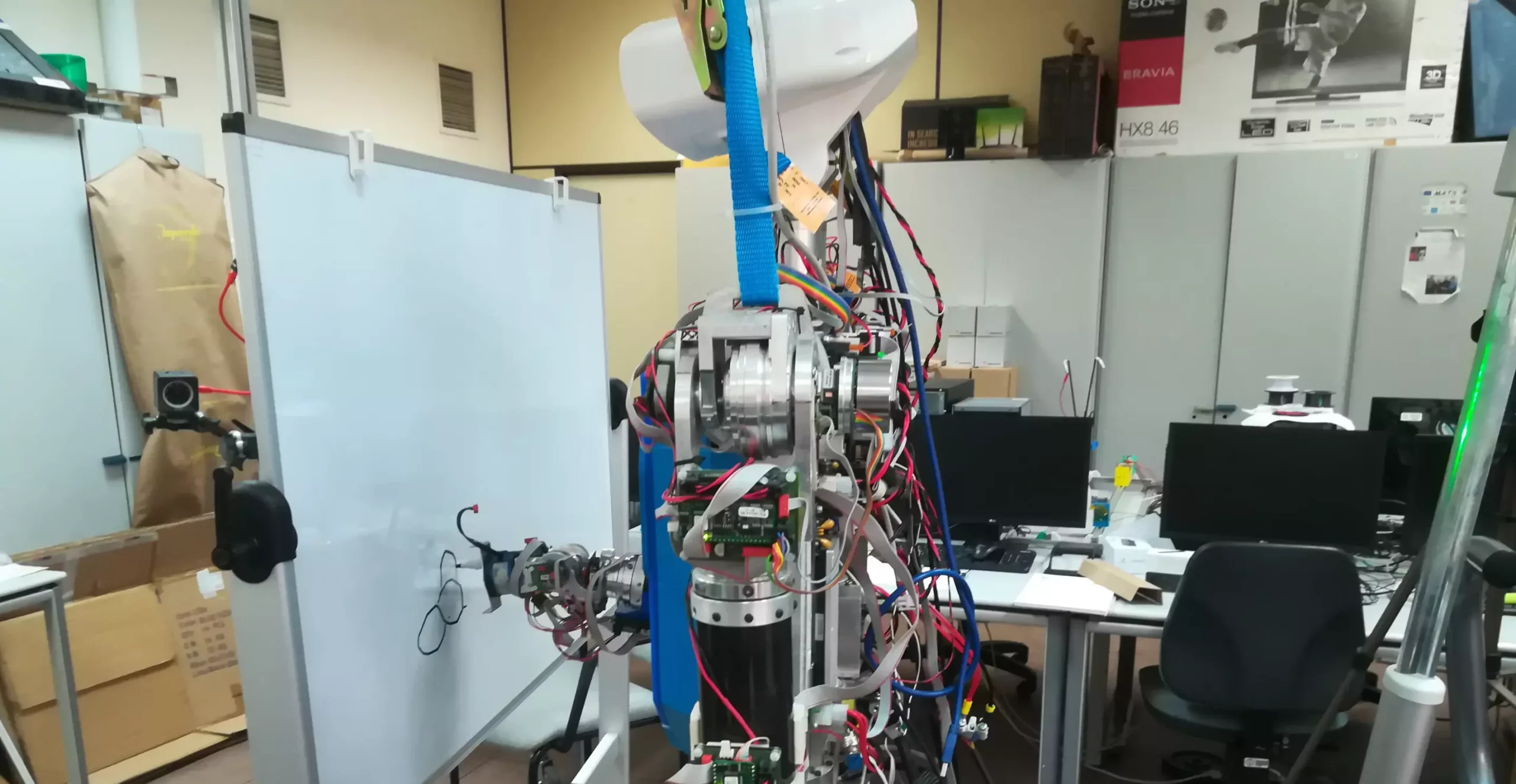
The continuous advancement of deep learning algorithms and generative models has paved the way for the production of highly impressive AI-generated artistic content. While most AI-generated art is typically created by algorithms and computational models, researchers at Universidad Complutense de Madrid (UCM) and Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) have taken a step further. They have developed a groundbreaking deep learning-based model that enables a humanoid robot to sketch pictures, mirroring the creative process of a human artist.
The study, published in Cognitive Systems Research, demonstrates how robots can actively engage in creative processes. Co-author of the paper, Raúl Fernandez-Fernandez emphasized the aim to intrigue both the scientific community and the general public with the project. The team envisioned a robot application that could shock viewers by engaging in art creation, thus leading to the concept of a humanoid robot participating in artistic endeavors.
Unlike traditional robotic systems that reproduce pre-generated images, Fernandez-Fernandez and his team set out to redefine the capabilities of robots by utilizing deep reinforcement learning techniques to create sketches stroke by stroke, mimicking human-like drawing processes. The primary goal was not to generate complex paintings but to enhance the control stage of painting robot applications.
Over the past years, the researchers have focused on developing sophisticated algorithms to plan the actions of creative robots effectively. Their latest paper builds upon previous research efforts, combining innovative approaches to advance the field. The study draws inspiration from past works related to training robotic painters using the Quick Draw! Dataset and incorporating Deep-Q-Learning for performing complex trajectories with emotional elements.
The new robotic sketching system introduced by the team is grounded on a Deep-Q-Learning framework initially introduced in a previous publication by Zhou and colleagues. The researchers enhanced this framework to meticulously plan robots’ actions, enabling them to perform intricate manual tasks across diverse environments. The neural network powering the system is compartmentalized into three interconnected parts for efficient feature extraction and painting position generation.
In addition to the neural network architecture, the researchers integrated distance-related and tool information channels to guide the training of the model, improving its sketching capabilities. To further enhance the system’s human-like painting skills, a pre-training step was introduced based on a random stroke generator. The team implemented double Q-learning to address overestimation issues and a customized reward function for model training purposes.
One of the notable challenges faced by the researchers was translating distances and positions observed in AI-generated images into a physical canvas. To tackle this issue, they created a discretized virtual space within the canvas, allowing the robot to map painting positions provided by the model accurately. This technological advancement marks a significant leap in integrating advanced control algorithms within real robot painting applications.
The recent advancements in robotic art showcased by Fernandez-Fernandez and his team serve as an inspiring example of how robots can create art in a manner that resembles human artists more closely. The researchers anticipate that their deep learning-based model will encourage further exploration and studies in the field, potentially leading to the development of control policies that empower robots to undertake increasingly complex tasks.
The fusion of deep learning algorithms, generative models, and robotic systems opens up a realm of possibilities for the future of artificial creativity. The innovative approach taken by Fernandez-Fernandez and his colleagues presents a pioneering step towards integrating robotic technology into the realm of artistry. By leveraging advanced control algorithms and deep reinforcement learning techniques, robots can now engage in creative processes that challenge the boundaries of traditional robotics. As we progress further into the age of AI and automation, the intersection of art and technology promises to yield groundbreaking innovations that redefine our understanding of creativity and human-machine interactions.


Leave a Reply