Cells form the foundation of all living organisms, and gaining insights into their inner workings has long been a pursuit of scientists. Yet, the examination of cellular mechanics — the very essence of how cells behave and react under various conditions — remains a challenge laden with complexity. Traditional methods for analyzing the internal properties of cells often come at a cost: they can destroy the very cells being observed, rendering the results both limited and destructive. This paradox in cellular research has stymied progress and left many questions unanswered, particularly regarding the mechanical properties that dictate a cell’s behavior.
Recent advancements from a team of researchers at the University of Göttingen could finally provide the clarity needed to unveil the mechanical dynamics occurring within cells. Their innovative approach, presented in a groundbreaking paper in *Nature Materials*, leverages the subtle, random movements of microscopic particles to glean insights about cellular interiors without causing damage. By focusing on the behavior of these particles, scientists are poised to uncover the mysteries of cell mechanics while preserving the integrity of the cells themselves.
A New Methodological Breakthrough
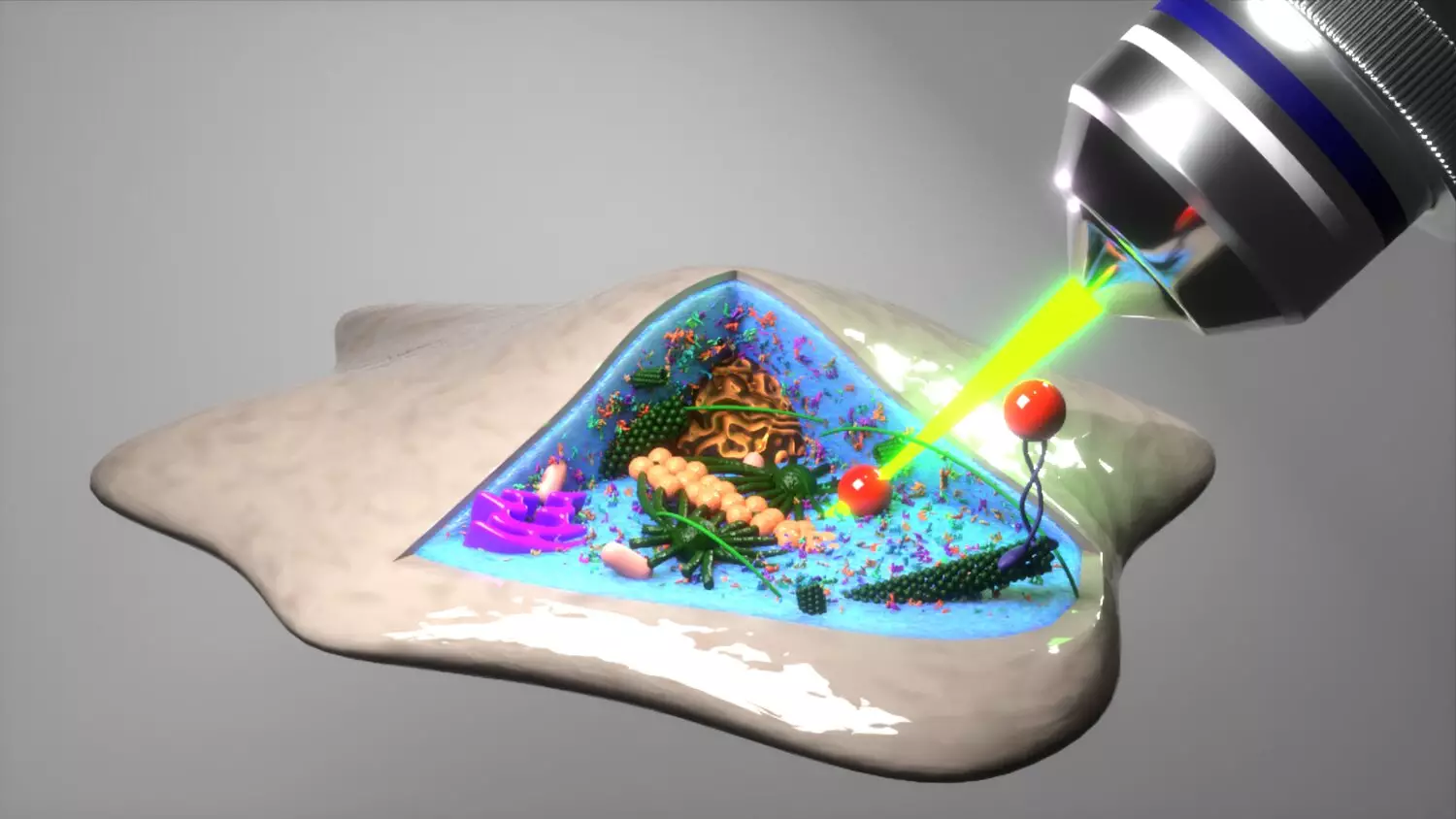
At the heart of this study lies the concept of “mean back relaxation” (MBR). This newly defined measure captures how microscopic particles within cells tend to return to their previous locations after wandering off due to random fluctuations – reminiscent of the behavior one might observe in a bouncing ball. Researchers used optical laser traps to simulate and confirm their predictions about these movements, achieving remarkable precision in the nanometer scale.
The implications of introducing MBR extend far beyond just describing movement; it allows for differentiation between various types of motion inside cells. Previously, scientists struggled to distinguish between forces exerted by a cell itself and those imposed by temperature-driven movements (like Brownian motion). With MBR, researchers can now pinpoint the active biological processes at play, offering a deeper understanding of cellular mechanics.
Impacts on Biology and Medicine
What makes these findings particularly significant is their applicability to live cells. The researchers faced uncertainty about whether their MBR technique could be applicable in a living context. However, the results they observed were astonishing and surpassed expectations. Professor Timo Betz, a lead experimenter, expressed his disbelief at how effectively MBR could describe cellular interiors using analytical techniques originally designed for simpler physical systems.
The potential benefits of understanding whether cells are soft, hard, or liquid can influence a range of biological and medical inquiries. From cancer research to tissue engineering, the ability to characterize the mechanical properties of cells accurately opens new doors for treatment strategies. Cells themselves can exhibit mechanical properties that vary significantly based on their state, and these variations can be crucial in understanding disease progression or recovery processes.
A Collaborative Effort Toward Discovery
The recent work by the Göttingen team underscores the power of interdisciplinary research in the sciences. Professor Matthias Krüger emphasizes this collaboration, noting that the convergence of theoretical understanding and experimental verification underpinned the study’s success. This juncture of different scientific disciplines facilitates advancements in both knowledge and technical capability, which are essential for overcoming the hurdles that have historically constrained cellular research.
As the study illustrates, the future of cell biology may very well thrive on innovative methodologies that prioritize non-invasive observation techniques. The ability to extract significant information from the movements of microscopic particles within cells heralds a new era in the study of life at its most fundamental level, bridging gaps that have long hindered scientific exploration.
As researchers continue to refine techniques like MBR, they stand on the brink of unlocking broader understanding — one that could lead not only to better science but also to improved health outcomes for communities worldwide. The journey into the microscopic world of cells promises to reveal not just how life functions at a cellular level, but also how we might better intervene when things go awry.


Leave a Reply