In a groundbreaking development, researchers from the University of Minnesota have introduced a novel tool that enables the measurement of ethane from space. This innovative approach has significant implications for enhancing our comprehension of fossil fuel emissions on a global scale.
Ethane, a compound commonly present in natural gas and utilized mainly in the production of plastics, plays a crucial role in the environmental impact of oil and gas extraction. By leveraging satellite-based technology to analyze infrared radiation emitted by Earth, researchers can assess how this radiation interacts with gases in the atmosphere, providing valuable insights into the abundance of these gases.
Research Findings
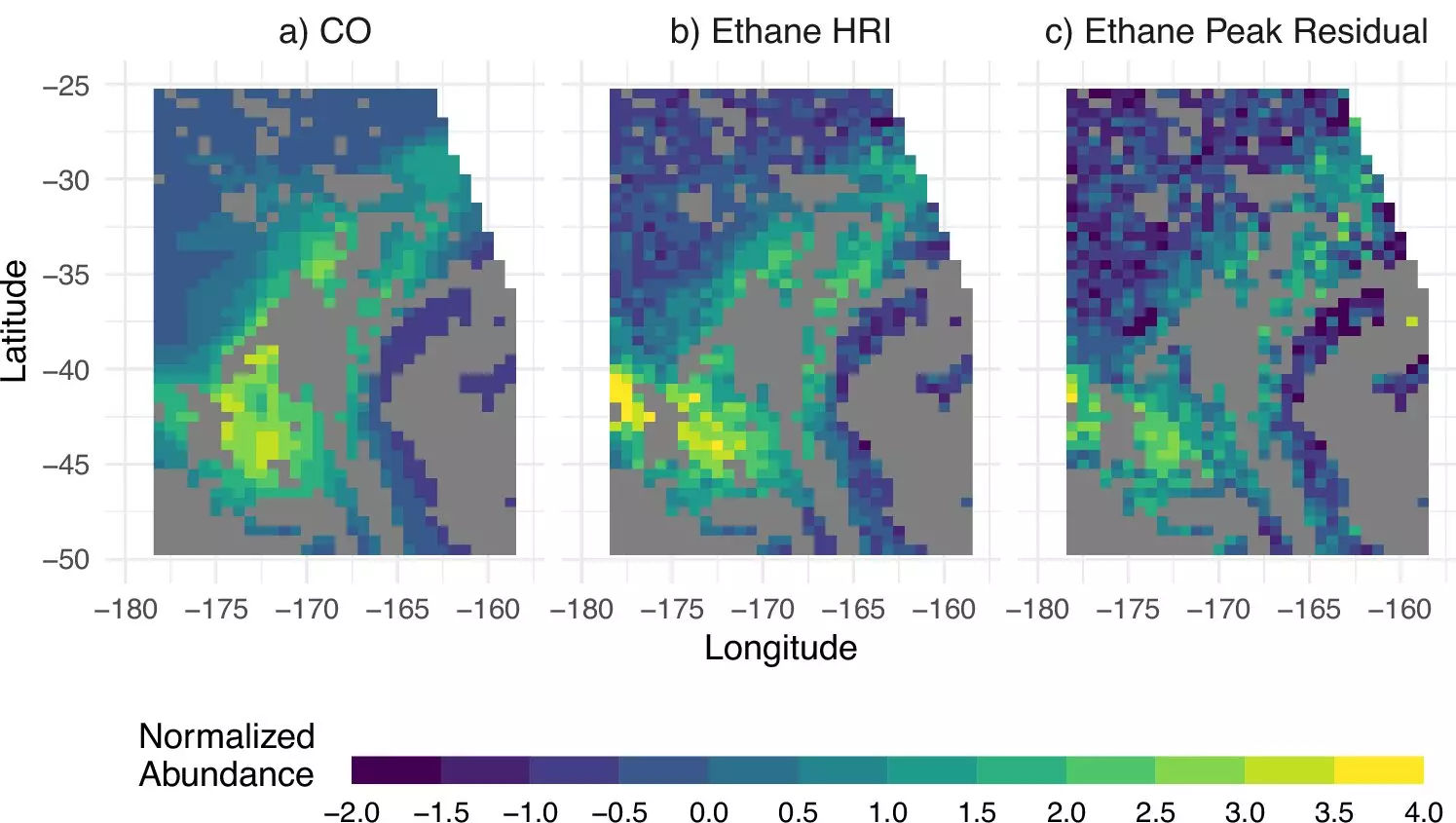
The team of experts employed a machine learning algorithm to ascertain atmospheric ethane concentrations based on satellite data. Through their analysis, they were able to map ethane levels across major oil and gas basins globally. Notably, the study revealed that the Permian Basin in western Texas and southeastern New Mexico exhibited the highest levels of persistent ethane emissions worldwide. Furthermore, the research indicated that ethane emissions from this region are significantly underestimated, highlighting the urgent need for accurate measurement tools.
By identifying key sources of ethane emissions and quantifying their impact, the research offers a critical foundation for addressing air quality degradation and climate change. With plans to ensure measurement continuity well into the 2030s and the deployment of additional instruments for enhanced monitoring, the potential for tracking and mitigating fossil fuel emissions is more promising than ever.
Future Directions
Lead author Jared Brewer emphasized the significance of this research in bridging the gap between current ethane emission estimates and the actual sources of pollution. As advancements in satellite technology continue to evolve, the ability to monitor ethane emissions globally and in real-time holds immense potential for driving proactive measures to combat environmental degradation.
The development of a tool to measure ethane from space represents a significant milestone in environmental research. By leveraging cutting-edge technology and innovative approaches, researchers are poised to revolutionize our understanding of fossil fuel emissions and pave the way for more effective climate action strategies.


Leave a Reply