The demand for environmentally friendly packaging is at an all-time high due to the ongoing plastic waste crisis. Research conducted by Srinivas Janaswamy, an associate professor of food chemistry at South Dakota State University, has shed light on how banana peels can be utilized to create biodegradable films as a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based plastics.
One of the biggest challenges with petroleum-based plastics is their lack of decomposition. Plastic packaging, such as plastic bags, takes up to 20 years to decompose, contributing to the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and the environment. With minimal recycling of plastic materials, finding a biodegradable alternative has become imperative to mitigate the adverse health and environmental impacts of plastic pollution.
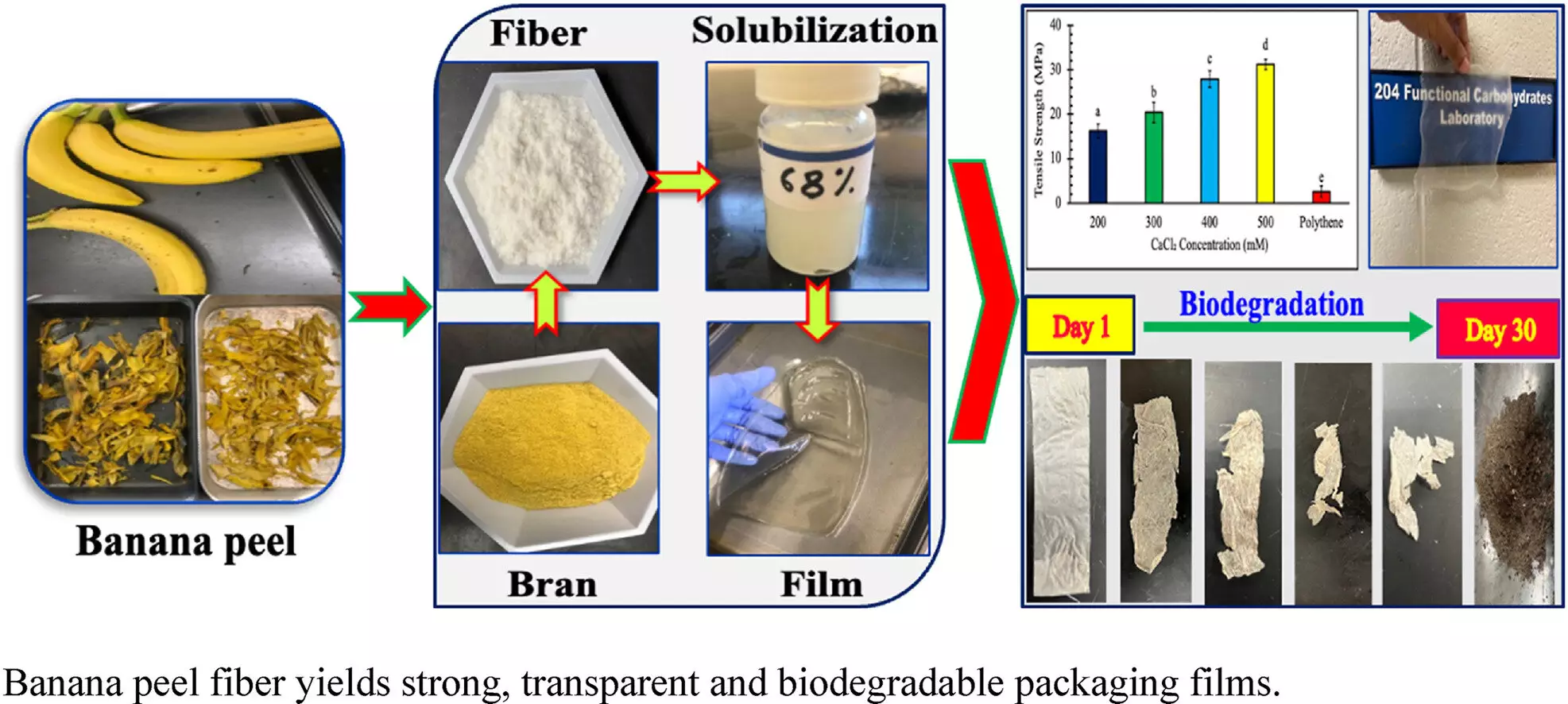
Bananas are one of the most widely consumed fruits globally, generating a significant amount of byproducts, primarily in the form of banana peels. Banana residue consists of lignocellulosic material, which serves as the key ingredient in creating biodegradable films. With approximately 36 million tons of banana peels discarded annually, there is enormous potential to repurpose this byproduct into sustainable packaging materials.
Janaswamy and his research team demonstrated how banana peels can be transformed into biodegradable films through a chemical treatment process. By extracting lignocellulosic fibers from banana peels and processing them into films, they were able to create packaging materials that decompose within 30 days under specific soil moisture conditions. These films exhibited high transparency and tensile strength, outperforming commercial grocery sack bags in terms of quality and durability.
The biodegradable films derived from banana peels offer several advantages over traditional plastic packaging materials. In addition to being environmentally friendly, these films are strong, transparent, and biodegradable, making them suitable for various food packaging applications. The use of banana peels as a raw material for packaging not only reduces environmental pollution but also provides financial benefits to the agricultural industry by utilizing a previously wasted resource.
The scalability and commercialization of banana peel-based biodegradable films present exciting opportunities for the packaging industry. Further research will focus on enhancing the flexibility of these films and refining the production process to meet the growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions. As consumer preferences shift towards eco-friendly products, the adoption of banana peel films as a packaging material could revolutionize the industry and contribute to reducing plastic waste on a global scale.
The innovative use of banana peels to develop biodegradable films represents a significant step towards addressing the plastic waste crisis and promoting sustainability in the packaging sector. By harnessing the inherent properties of banana peels and transforming them into viable packaging materials, researchers like Srinivas Janaswamy are paving the way for a more eco-conscious future.

Leave a Reply