In a remarkable leap forward for environmental monitoring, researchers from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have unveiled a cutting-edge microfluidic sensor system. This technology promises to revolutionize how we detect harmful heavy metals like mercury, lead, chromium, and copper in our water sources. Prof. Jiang Changlong, the project’s lead, emphasized that this development offers an unprecedented method for real-time water quality assessment, potentially safeguarding ecosystems and human health alike.
The Challenge of Heavy Metal Contamination
Heavy metals pose a formidable threat to both environmental and public health. Found in various forms in water supplies, these hazardous substances, including mercury and lead, are notoriously difficult to eliminate. Traditional detection methods are not only time-consuming but often target individual metals in succession, leaving a gap in timely responses to contamination. The urgency to innovate is clear: as industrial and urban pollution continues to escalate, so too does the necessity for efficient monitoring solutions.
Smart Design and Functionality of Microfluidic Sensors
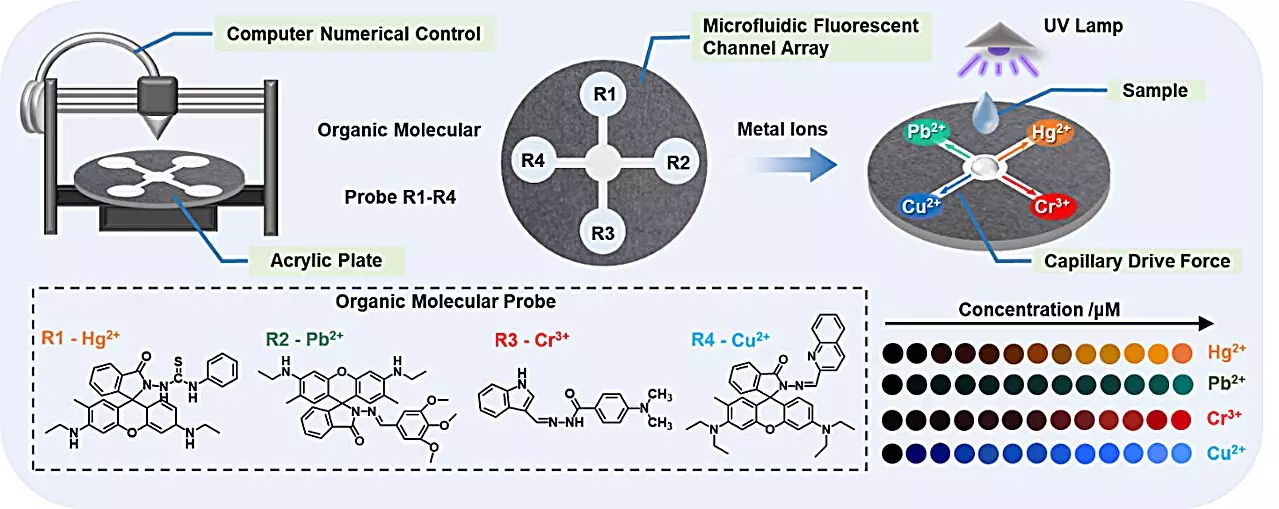
The core advantage of the new sensor array lies in its sophisticated design. By harnessing the principles of capillary action and the properties of hydrophobic acrylic surfaces, the researchers created a network of microfluidic channels. This allows for seamless movement of liquids, facilitating simultaneous analysis of multiple contaminants. Traditional methods fail to offer such efficiency, making this innovation a potential game-changer for environmental monitoring.
Fluorescence: A Visual Breakthrough
At the heart of these microfluidic sensors are organic fluorescent probes, chosen for their unparalleled sensitivity and specificity. These affordable probes intelligently bind to designated heavy metal ions, lighting up to reveal their presence. By creating microfluidic chip arrays with distinct probes for each type of metal, the researchers have created a potent visual detection system. Such a feature not only enhances the efficiency of testing but also provides immediate, understandable data for users, making it an accessible tool for various stakeholders, from environmental scientists to water safety regulators.
User-Friendly Technology Meets Science
An additional standout characteristic of this innovation is its compatibility with everyday technology. The detection system operates in conjunction with a smartphone equipped with color recognition capabilities, allowing users to visualize and quantify contamination levels in real-time. This integration of advanced scientific detection with common technology democratizes access to water quality monitoring, empowering individuals and communities to take proactive measures against water pollution.
Implications for Health and Environment
This pioneering work signifies a pivotal step toward ensuring safe drinking water and protecting our ecosystems from the detrimental impacts of heavy metal pollution. As this technology continues to develop and undergo refinement, it holds the promise not only of real-time detection but also of fostering broader awareness around water safety issues. Ultimately, this innovation could lead to a deeper understanding of water quality at both community and global levels, heralding a new era of environmental stewardship.

Leave a Reply