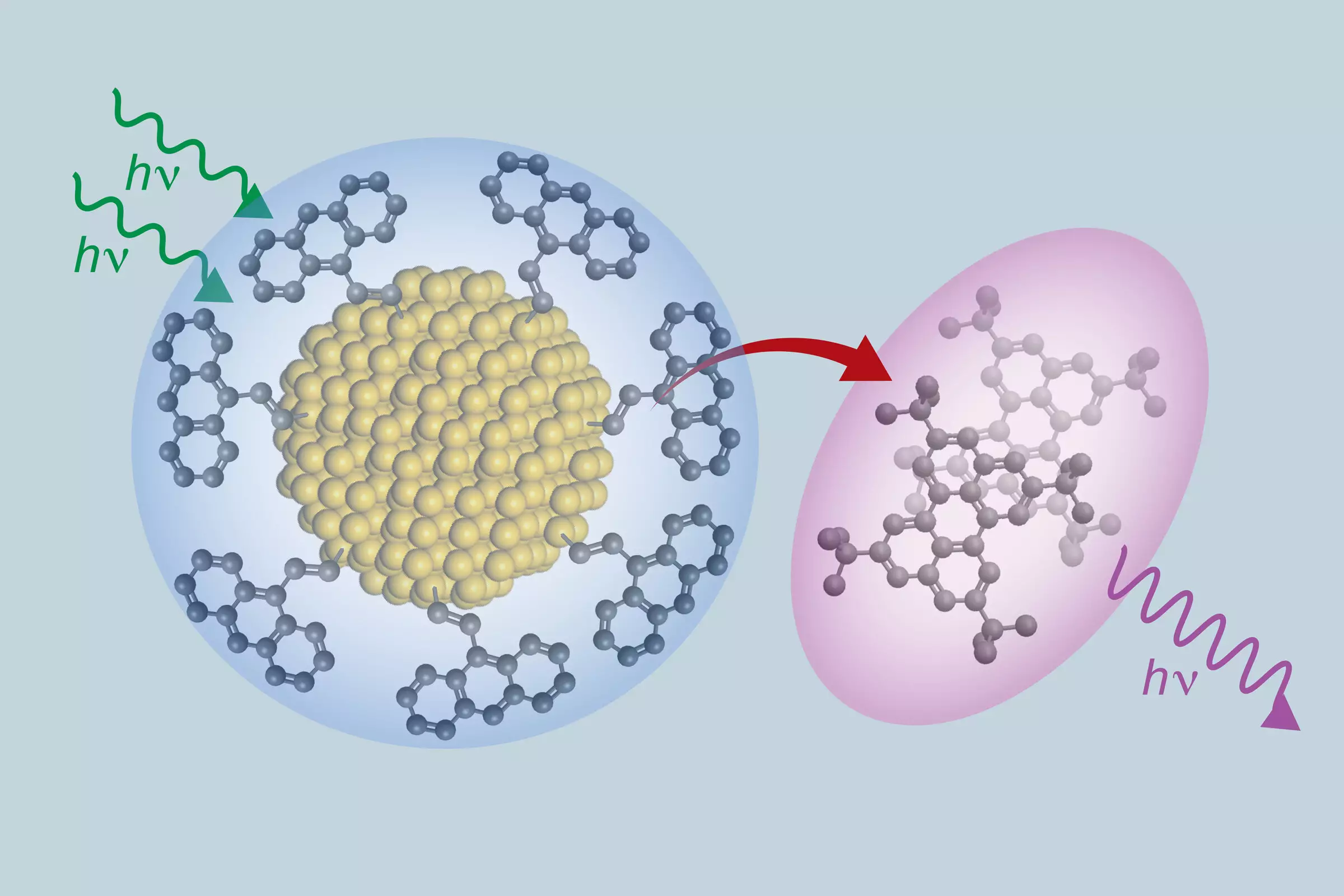
A group of scientists and engineers, including researchers from The University of Texas at Austin, have developed a new class of materials that can absorb low energy light and turn it into higher energy light. The group achieved this through combining ultra-small silicon nanoparticles and organic molecules, closely related to those used in OLED TVs. The composite created can move electrons efficiently between its inorganic and organic components, which could potentially lead to more efficient solar panels, better night vision goggles and more accurate medical imaging. The research is published in the journal Nature Chemistry.
Composite Design
The team’s new process allows them to take two different substances, silicon and organic molecules, and bond them strongly enough to create a new hybrid material with unique properties. Composites, which are made up of two or more components, can achieve distinct properties when combined. For example, carbon fiber and resins are used to create lightweight airplane wings, racing cars, and sporting products. In this case, the inorganic and organic components were combined to show a unique interaction with light.
Applications
One of the most significant properties of this material is its ability to convert long-wavelength photons, typically found in red light, into short-wavelength blue or ultraviolet photons, which are usually responsible for making sensors work. This means the material could be useful in various applications, including bioimaging, light-based 3D printing, and light sensors that can help self-driving cars travel through fog.
Furthermore, this technology could potentially increase the efficiency of solar cells by capturing near-infrared light that would typically pass through them. When optimized, capturing low energy light could reduce the size of solar panels by up to 30%.
Research Team
The research team, which includes scientists from the University of California Riverside, University of Colorado Boulder, and University of Utah, has been working on light conversion for several years. In a previous paper, they successfully connected anthracene, an organic molecule that can emit blue light, with silicon, a material used in solar panels and many semiconductors.
The team developed a new method for forging electrically conductive bridges between anthracene and silicon nanocrystals to amplify the interaction between the two materials. The resulting strong chemical bond increases the speed with which the two molecules can exchange energy, almost doubling the efficiency in converting lower energy light to higher energy light, compared with the team’s previous breakthrough.
This new composite of ultra-small silicon nanoparticles and organic molecules shows great potential for various applications, from better night vision goggles, to more efficient solar panels, and more accurate medical imaging. The ability to convert low energy light into higher energy light is a significant breakthrough that could lead to many new technologies. With ongoing research, this new method of designing materials could revolutionize the way we think about composites and their uses.


Leave a Reply