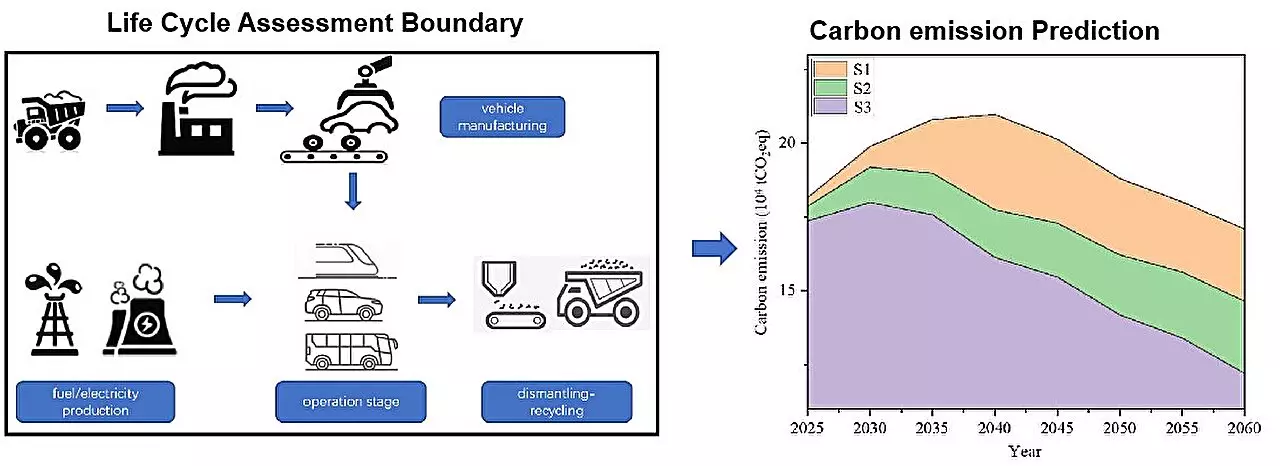
Transportation is a significant contributor to global carbon emissions, ranking as the third largest source. Governments worldwide recognize the urgency of addressing this issue. High-speed railways (HSR) have emerged as a promising solution for intercity transportation due to their high degree of electrification. However, a lack of substantial data has hindered efforts to understand the extent of carbon reduction that can be achieved through high-speed rail travel and the most effective regulatory strategies for various transportation modes. In a recent study published in the journal High-Speed Railway, researchers from Beijing Jiaotong University have aimed to fill this research gap by thoroughly analyzing the entire life cycle carbon emissions of vehicles.
Lead author of the study, Lu Yintao, emphasizes the importance of evaluating carbon emissions throughout a product’s entire life cycle. This approach encompasses the complete journey of a product or tool, from the utilization of natural resources to its eventual return to nature. Adopting this perspective provides a more accurate assessment of a product’s environmental impact, reflecting the holistic life process of human beings.
Road transportation has historically been the primary mode of passenger travel, encompassing private cars, buses, and railways, each utilizing different energy sources like gasoline and electricity. To determine the most effective transportation combinations in reducing carbon emissions during travel, the study utilizes a per-person-per-kilometer evaluation unit. This approach considers various factors and energy sources involved in each mode of transportation. Unlike previous studies that focus on infrastructure, this research examines the complete life cycle of vehicles and fuels.
The study’s findings reveal that high-speed rail demonstrates significant carbon emission reduction compared to private vehicles and buses. Compared to private vehicles, the carbon emission intensity of high-speed rail stands at only 24%-32%. In comparison to buses, high-speed rail showcases a reduction between 47% to 89%. This disparity highlights the tremendous potential of high-speed rail travel in substantially decreasing carbon emissions.
In addition to contributing to carbon reduction efforts in transportation, this study also offers valuable insights for vehicle manufacturers. The research emphasizes the materials that should be prioritized during production, considering their significant implications for carbon reduction. By focusing on materials that have lower carbon footprints, manufacturers can take a crucial step towards sustainable vehicle production.
The senior author of the study, Yao Hong, underscores the continuous nature of carbon emissions during transportation and their role in the entire life cycle of carbon emissions. It is her hope that this research will provide theoretical support for China’s ongoing carbon reduction efforts in the transportation sector. Detailed insights into the carbon emission characteristics of various transportation modes can inform policy decisions and drive the transition towards more sustainable transportation systems.
This study represents a comprehensive analysis of the impact of high-speed rail travel on carbon emissions. Its findings emphasize the need for sustainable transportation alternatives and provide valuable information for policymakers and vehicle manufacturers. By adopting a whole-life cycle perspective, researchers have shed light on the significant carbon reduction potential of high-speed rail, paving the way for a greener future in the transportation sector.

Leave a Reply