Researchers at Columbia University and the Max Planck for the Structure and Dynamics of Matter have made an exciting discovery that could revolutionize nonlinear optics. By pairing laser light with crystal lattice vibrations, they have found a way to enhance the nonlinear optical properties of a layered 2D material. This research, published in the journal Nature Communications, opens up new possibilities for generating new optical frequencies and amplifying certain optical effects.
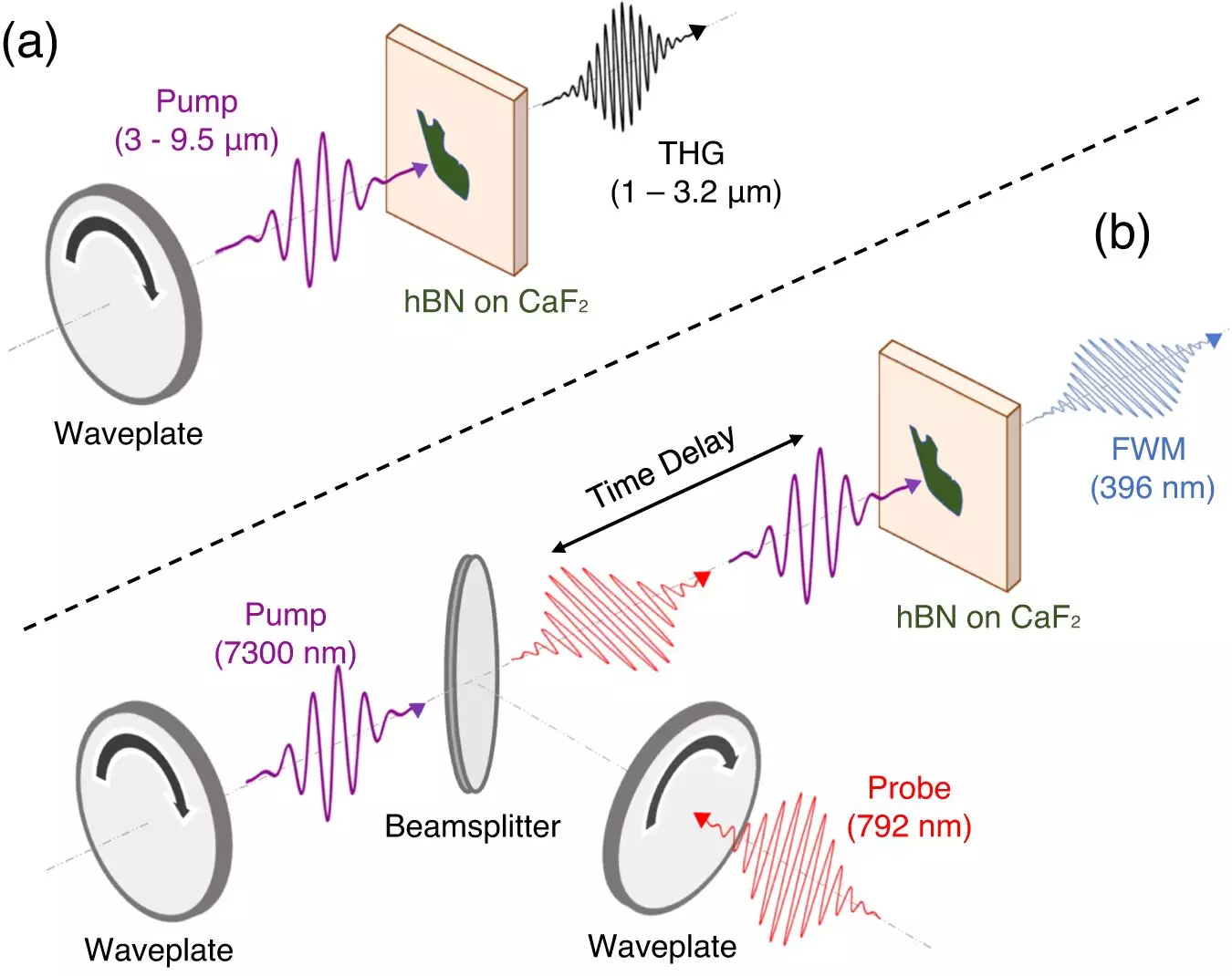
In this study, the researchers used hexagonal boron nitride (hBN), a 2D material similar to graphene. hBN is known for its unique quantum properties and can be peeled into thin layers. One of the advantages of hBN is its stability at room temperature. Additionally, the atoms in hBN, boron, and nitrogen, are very light, resulting in rapid vibrations. These atomic vibrations, known as phonons, have specific resonances, and the team focused on the optical phonon mode vibrating at 41 THz, corresponding to a wavelength of 7.3 µm in the mid-infrared regime of the electromagnetic spectrum.
While mid-infrared wavelengths are typically considered short and high energy, the team approached the study from the perspective of crystal vibrations. In this context, mid-IR wavelengths are seen as long and low energy. Most optics research with lasers focuses on the visible to near-IR range. By tuning their laser system to hBN’s frequency of 7.3 µm, the researchers were able to simultaneously drive the phonons and electrons of the hBN crystal, effectively generating new optical frequencies. This achievement is a major breakthrough in nonlinear optics, where the goal is to efficiently generate new frequencies from a medium.
The experimental team, consisting of Cecilia Chen, Jared Ginsberg, and Mehdi Jadidi, utilized commercially available, table-top mid-infrared lasers to explore the phonon-mediated nonlinear optical process of four-wave mixing. This process allowed them to generate light close to even harmonics of an optical signal. The results were remarkable, with the researchers observing a greater than 30-fold increase in third-harmonic generation compared to previous experiments conducted without exciting the phonons. The team’s findings were further supported by theoretical work led by Professor Angel Rubio’s group at Max Planck.
The implications of this research are significant. By amplifying the natural phonon motion with laser driving, the team has demonstrated that nonlinear optical effects can be greatly enhanced, leading to the generation of new frequencies. This breakthrough opens up possibilities for applications in fields such as telecommunications, data storage, and laser technology. Furthermore, the researchers plan to further explore the modification of hBN and similar materials using light, paving the way for future advancements in the field.
The collaboration between Columbia University and the Max Planck for the Structure and Dynamics of Matter has resulted in a groundbreaking discovery in nonlinear optics. By manipulating crystal lattice vibrations through laser light, the research team has successfully enhanced the nonlinear optical properties of a layered 2D material. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize various industries and pave the way for new technological advancements. The future looks promising as researchers continue to explore the possibilities of harnessing the power of laser-driven crystal vibrations.


Leave a Reply