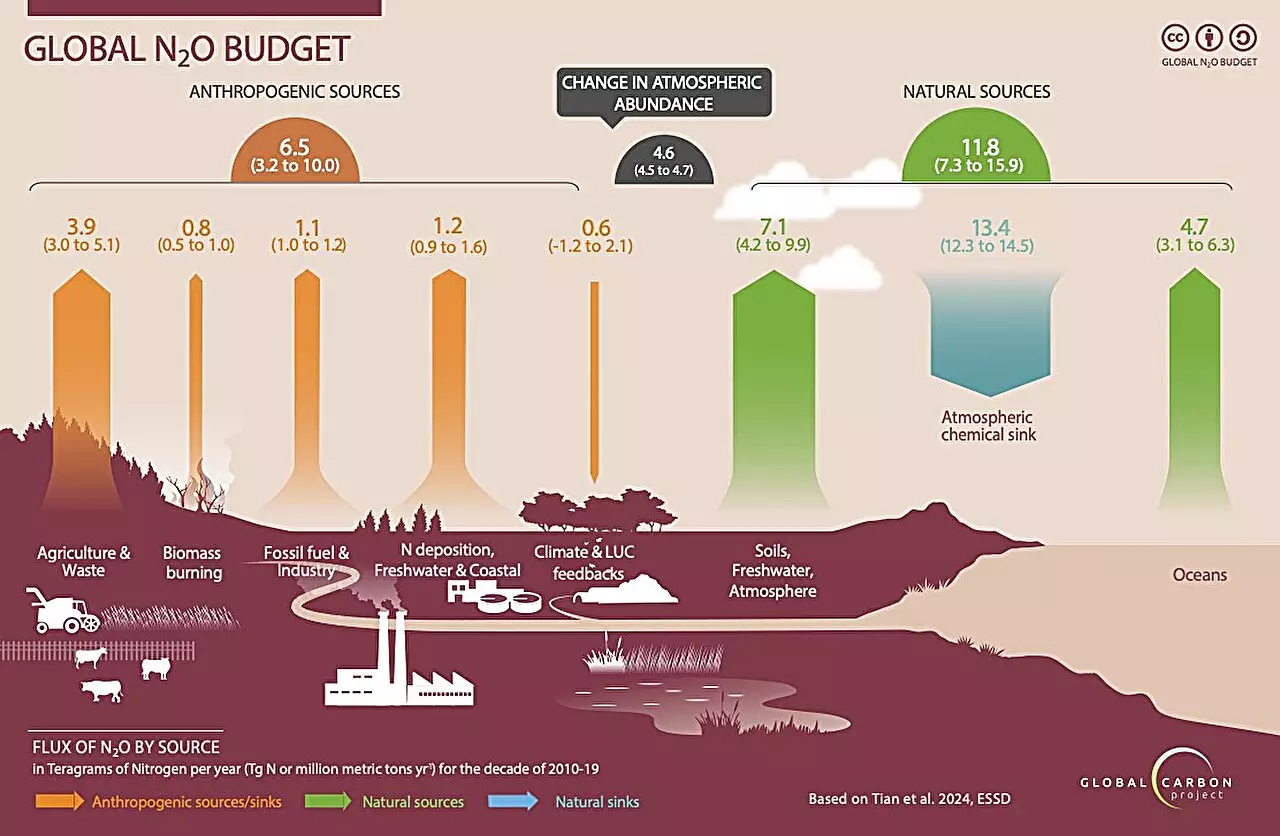
The alarming increase in nitrous oxide emissions has been a major concern for researchers studying its impact on the environment. The recent report by the Global Carbon Project reveals that between 1980 and 2020, over 10 million metric tons of nitrous oxide were released into the atmosphere. This greenhouse gas is even more potent than carbon dioxide and methane, making it a significant contributor to global warming.
The study highlights that agricultural activities are responsible for 74% of human-driven nitrous oxide emissions, with chemical fertilizers and animal waste on croplands being the primary sources. The use of these practices has resulted in a 67% increase in emissions from 1980 to 2020. This rise in emissions poses a serious threat to the environment and exacerbates climate change.
Lead author of the report, Hanqin Tian, emphasizes the urgent need to decrease nitrous oxide emissions to limit global temperature rise to 2°C, as outlined in the Paris Agreement. The concentration of atmospheric nitrous oxide has already reached 336 parts per billion in 2022, far exceeding predictions by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. This rapid increase in emissions is alarming, especially when global greenhouse gases should be declining towards net zero emissions.
The report underscores the importance of implementing strategies to reduce nitrous oxide emissions. The use of commercial nitrogen fertilizers and animal waste has significantly contributed to the rise in emissions over the past four decades. Without effective mitigation efforts, the consequences of continued emissions of this powerful greenhouse gas could be catastrophic for the planet.
Established in 2001, the Global Carbon Project has been at the forefront of analyzing the impact of human activities on greenhouse gas emissions. The organization advocates for improved agricultural practices to limit the use of nitrogen fertilizers and animal waste, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions and water pollution. By targeting high-emission regions and activities, mitigation efforts can be more effective in addressing the ongoing rise in nitrous oxide emissions.
The rising levels of nitrous oxide emissions pose a significant threat to the environment and the planet as a whole. Urgent action is needed to curb these emissions and mitigate their impact on global warming. By implementing sustainable agricultural practices and reducing the use of chemical fertilizers, we can work towards a cleaner and greener future for generations to come.


Leave a Reply