Ammonia production plays a crucial role in agriculture by providing the necessary fertilizer for crop growth. However, the traditional method of producing ammonia through the Haber-Bosch process is not sustainable. This process requires a significant amount of energy and results in the production of greenhouse gases, specifically carbon dioxide. In light of these challenges, researchers are exploring innovative ways to produce ammonia sustainably, with a focus on harnessing sunlight as a renewable energy source.
The Role of Nitrogenase Enzyme
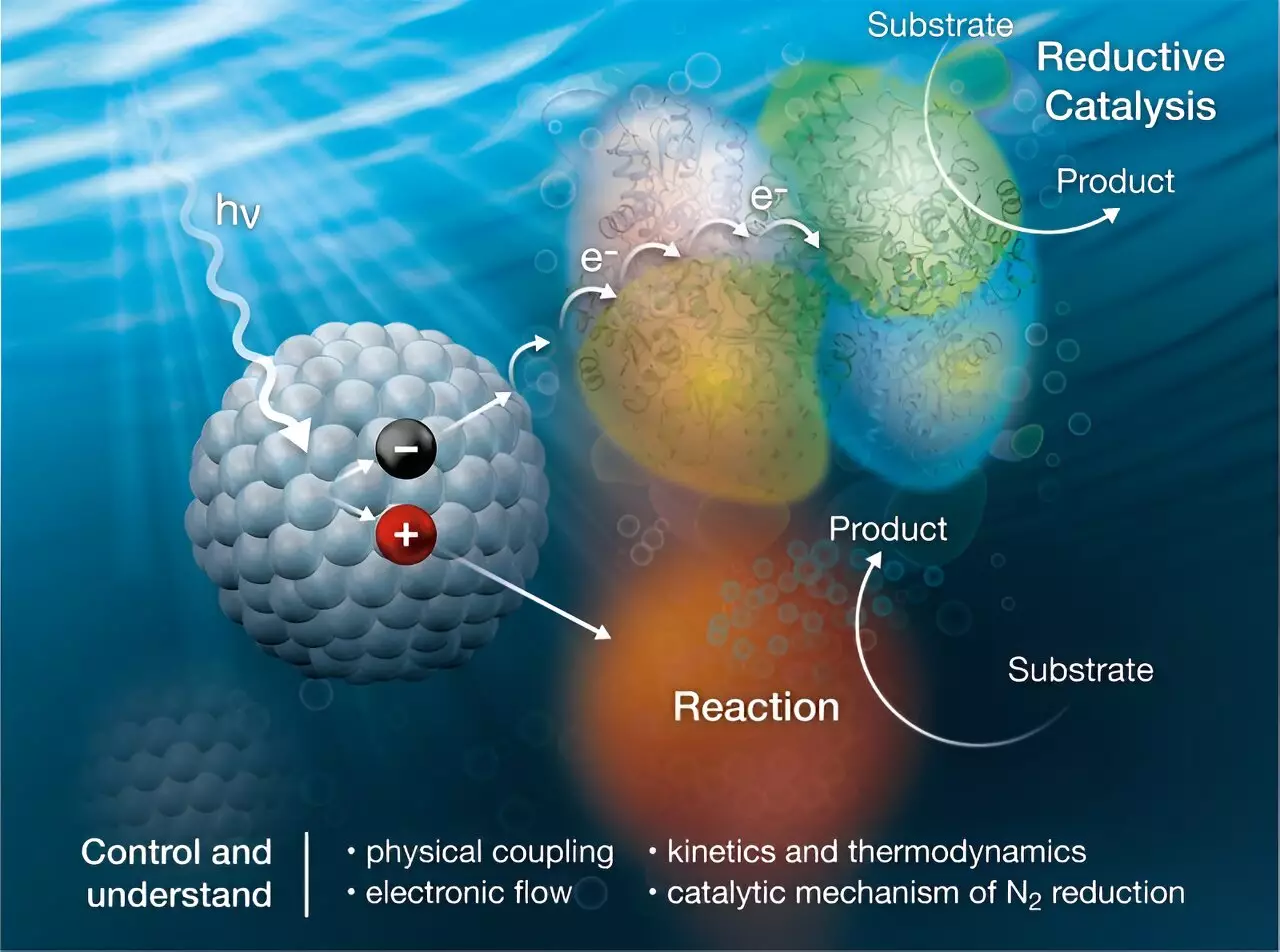
One promising approach involves utilizing the nitrogenase enzyme, which is capable of catalyzing the conversion of dinitrogen gas to ammonia using the energy stored in adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is a universal energy carrier found in all living organisms. By coupling nanocrystals to nitrogenase, researchers have developed a biohybrid system that can utilize sunlight to drive the ammonia production reaction. This novel approach not only reduces the energy requirements for ammonia production but also eliminates the generation of greenhouse gases.
The biohybrid system developed by scientists offers a sustainable solution for producing ammonia. By using sunlight to transfer charge to the nitrogenase enzyme, the nanocrystals facilitate the reduction of dinitrogen gas to ammonia. This process not only minimizes the carbon footprint associated with traditional Haber-Bosch ammonia production but also allows for the localized production of ammonia fertilizers, reducing emissions from transportation.
Understanding the Mechanism
To optimize the biohybrid system, researchers have focused on understanding how nanocrystals bind to the nitrogenase enzyme and facilitate the transfer of electrons to the FeMo-cofactor, a crucial metal cluster within the enzyme. By studying the interaction between nanocrystals and the enzyme, scientists can gain valuable insights into the mechanism of ammonia production and develop strategies to enhance the efficiency of the process.
Moving forward, researchers aim to further investigate the biohybrid system to uncover the intricacies of the ammonia production reaction. By trapping and analyzing reaction intermediates using advanced spectroscopy techniques, scientists can elucidate the activation energies of the reaction steps and develop a comprehensive kinetic model of the nitrogen reduction process. This foundational research paves the way for the continued development of sustainable and efficient methods for producing ammonia using sunlight.
The utilization of sunlight as an energy source for ammonia production represents a promising avenue for sustainable agriculture. By harnessing the power of nanocrystals coupled with the nitrogenase enzyme, researchers have made significant strides towards developing a low-energy process that minimizes greenhouse gas emissions. The future of ammonia production lies in innovative biohybrid systems that leverage renewable energy sources to meet the demands of a growing population while preserving the health of the planet.


Leave a Reply