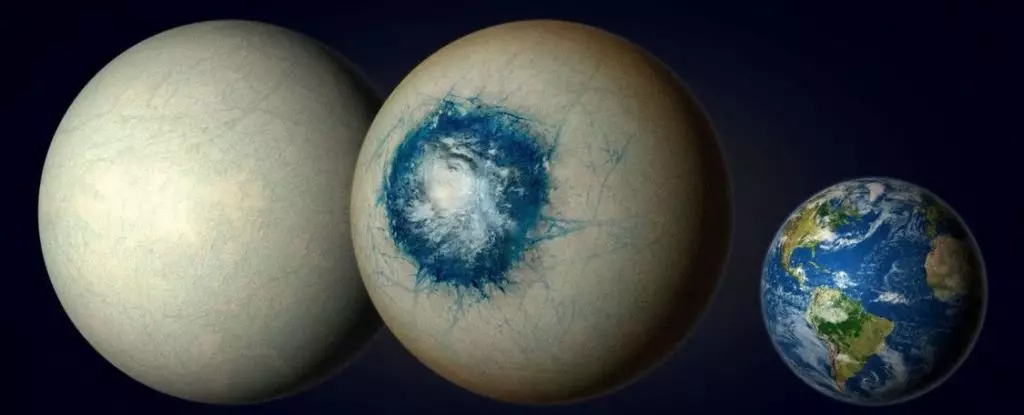
In 2017, astronomers made an exciting discovery when they identified an exoplanet known as LHS-1140b as one of the most promising locations for life to exist outside our Solar System. However, recent observations have made this alien world even more intriguing and bizarre. Scientists now believe that LHS-1140b may be an ‘eyeball’ planet, characterized by a global ocean covered in ice, with a single, iris-like region gazing perpetually at its host star.
Despite its unusual features, LHS-1140b presents a unique opportunity for researchers to investigate the possibility of liquid water on an alien world beyond our Solar System. With a radius 1.73 times that of Earth and 5.6 times its mass, LHS-1140b is classified as a terrestrial world, albeit slightly larger than our home planet. Unlike Earth, LHS-1140b orbits its star at a much closer distance, completing a full orbit in just under 25 days. While such proximity would be detrimental if the star resembled our Sun, LHS-1140b’s star is a cool, dim, red dwarf, placing the exoplanet within the habitable zone.
Challenges and Opportunities
Although being within the habitable zone is a promising sign, it does not guarantee the presence of conditions conducive to life. To determine the chemical composition of LHS-1140b’s atmosphere, scientists have turned to the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) for assistance. Through careful observation of the starlight passing through the exoplanet’s atmosphere, researchers have detected the presence of nitrogen, a key component of Earth’s atmosphere.
The Mystery of LHS-1140b
Given its tidally locked nature, with one side perpetually facing the star, LHS-1140b’s global ocean may not resemble what we envision. The side facing away from the star could be frozen, while the region in direct sunlight could host a balmy temperature of 20 degrees Celsius (68 degrees Fahrenheit), potentially supporting a thriving marine ecosystem. While the exact circumstances on LHS-1140b remain uncertain, it stands as the most promising candidate for hosting an exotic alien ecosystem beyond our Solar System.
As scientists strive to unlock the mysteries of LHS-1140b, they acknowledge the challenges ahead in confirming the presence of an Earth-like atmosphere on this distant world. With the capabilities of the James Webb Space Telescope pushed to their limits, researchers are eager to gather more data to validate their initial findings. The search for life beyond our Solar System continues, with LHS-1140b standing out as a beacon of hope for discovering alien ecosystems and expanding our understanding of the universe.

Leave a Reply