
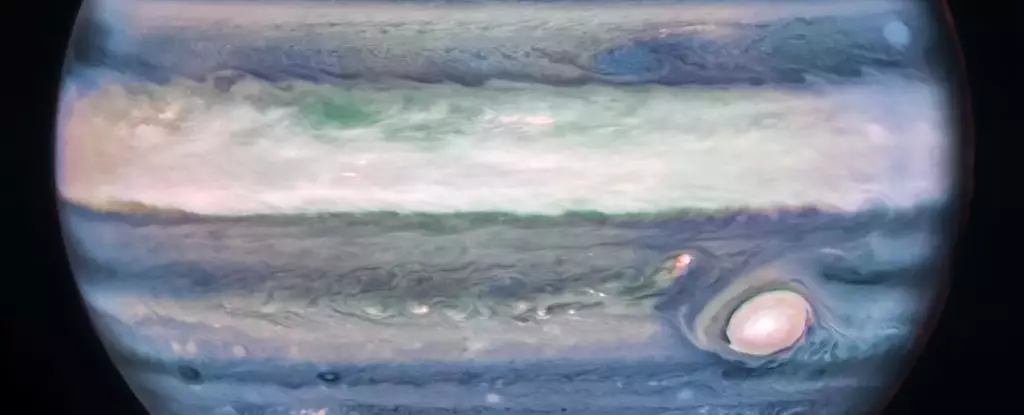
Jupiter, the second-largest object in the Solar System, continues to astound scientists with its enigmatic atmospheric phenomena. Despite numerous missions to explore this massive planet, new features are being uncovered. Recently, using the advanced infrared James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), researchers have identified a high-speed jetstream roaring around Jupiter’s equator. This unexpected finding could enhance our understanding of the peculiar weather dynamics in the Jovian system.
Jupiter’s atmosphere is a captivating spectacle. With alternating zones and belts, characterized by light and dark clouds respectively, the planet showcases a chaotic and mysterious environment. These bands not only rotate at different altitudes but also move in opposite directions, creating a mesmerizing display. Despite our efforts, comprehending the reasons behind these atmospheric features remains challenging.
By observing Jupiter in different wavelengths, scientists can uncover details that are invisible in the optical range. For instance, Jupiter exhibits the most powerful aurorae in the Solar System, uniquely emitting in ultraviolet light. The James Webb Space Telescope, with its state-of-the-art infrared capabilities, has transformed our understanding of the giant planet. A recent near-infrared image revealed unexpected clarity, providing a fresh perspective on Jupiter’s upper atmosphere.
Through meticulous analysis of the JWST images, astronomers detected a jetstream previously concealed within a hazy region. The newly exposed, high-speed stream races approximately 40 kilometers above Jupiter’s cloud tops, hurtling at an astonishing velocity of 515 kilometers per hour. This revelation could have significant implications for unraveling the intricate patterns of Jupiter’s weather. Comparing the lower cloud levels, observed by the Hubble Space Telescope, researchers noted the jetstream’s velocity to be double that of the surrounding winds. Furthermore, they discovered small-scale storm features that appeared and disappeared between rotations, suggesting the presence of vertical shears. This correlation indicates that the jetstream may contribute to observable weather patterns on Jupiter.
The newfound jetstream has unveiled a repeatable pattern of winds and temperatures in Jupiter’s equatorial stratosphere, distinct from the lower atmospheric phenomena observed at other wavelengths. These revelations provide opportunities for deeper investigations into the nature of Jupiter’s weather. Planetary scientist Leigh Fletcher from the University of Leicester, UK, emphasizes the complexity of Jupiter’s weather system and its potential for further research.
As scientists continue to explore Jupiter’s fascinating atmosphere, new surprises await. The discovery of a high-speed jetstream using the James Webb Space Telescope has shed light on a previously elusive feature. With this newfound insight, researchers can investigate the intricate weather patterns of Jupiter and further unravel the mysteries of this enigmatic giant planet.
Cells form the foundation of all living organisms, and gaining insights into their inner workings…
Mosquitoes are not just an irritating nuisance; they are deadly vectors that transmit a range…
In the quest for sustainable living, consumers often hold fast to the belief that glass…
For over a century, the astral mystery surrounding Barnard's Star, a unique red dwarf just…
In the realm of catalysis, particularly in the context of oxygen evolution reactions (OER), understanding…
Recent research has illuminated a groundbreaking connection between blood donation frequency and the health of…
This website uses cookies.