
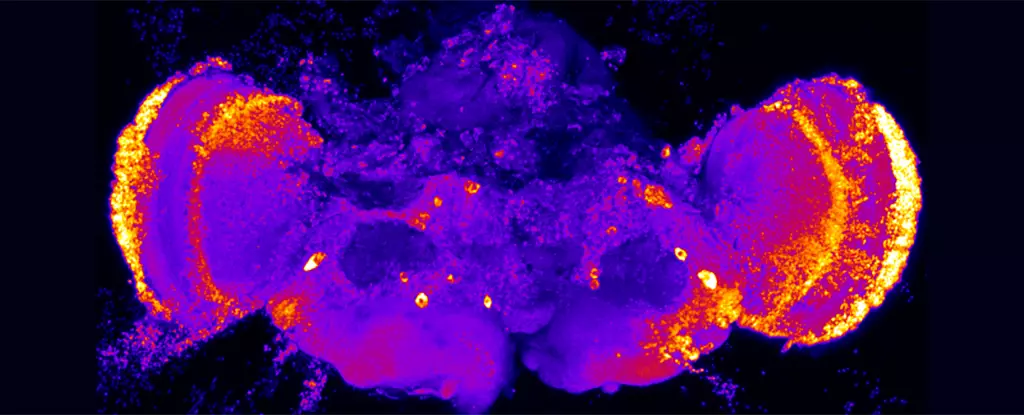
Alzheimer’s disease is a devastating neurodegenerative condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Recent research conducted by a team of researchers from Pennsylvania State University has shed light on a potential target for new drug therapies aimed at stopping Alzheimer’s in its early stages. The focus of this study was on heparan sulfate-modified proteoglycans (HSPGs), which are proteins found on the surface of animal cells and play a crucial role in regulating cell growth and cell environment interactions.
The study revealed that HSPGs are involved in essential cellular processes such as autophagy, cell energy production, and lipid buildup, all of which are disrupted in certain types of dementia, including Alzheimer’s. By manipulating the function of HSPGs, the researchers observed a reversal of dementia-related damage in cell repair processes and a halt in neuron death. Additionally, blocking the production of chains of heparan sulfate in human cells affected a significant number of genes associated with the later stages of Alzheimer’s. This suggests that HSPGs may play a role in different stages of disease progression.
While the research is still in its early stages, the findings offer a potential avenue for developing new drugs to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Targeting the enzymes responsible for producing heparan sulfate could be a viable strategy for blocking neurodegeneration in humans. With the global number of dementia cases expected to double in the next 20 years, the development of effective treatments for Alzheimer’s is more crucial than ever.
One of the challenges in developing treatments for Alzheimer’s is the complex nature of the disease, with multiple factors believed to contribute to its onset. Researchers are still working to understand the earliest cellular changes associated with Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. By identifying common pathways shared across these conditions, scientists hope to uncover new insights into disease mechanisms and potential treatment targets.
The study on HSPGs and their potential role in treating Alzheimer’s disease represents a significant step forward in the search for effective therapies. While further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms involved and develop targeted drugs, the findings offer hope for the future of Alzheimer’s treatment. By uncovering the early cellular changes associated with neurodegenerative diseases, researchers are paving the way for new strategies to combat these devastating conditions.
Foreign direct investment (FDI) in developing nations has long been heralded as a path to…
As spring beckons in April and May, stargazers have the unique opportunity to witness nature's…
Active matter, a term that refers to systems where individual components can consume energy to…
In a groundbreaking development, a research team led by Prof. Chen Changlun at the Hefei…
The inevitability of aging is experienced differently across individuals, influenced by a complex interplay of…
When we delve into the cataclysmic events that led to the destruction of Pompeii almost…
This website uses cookies.