
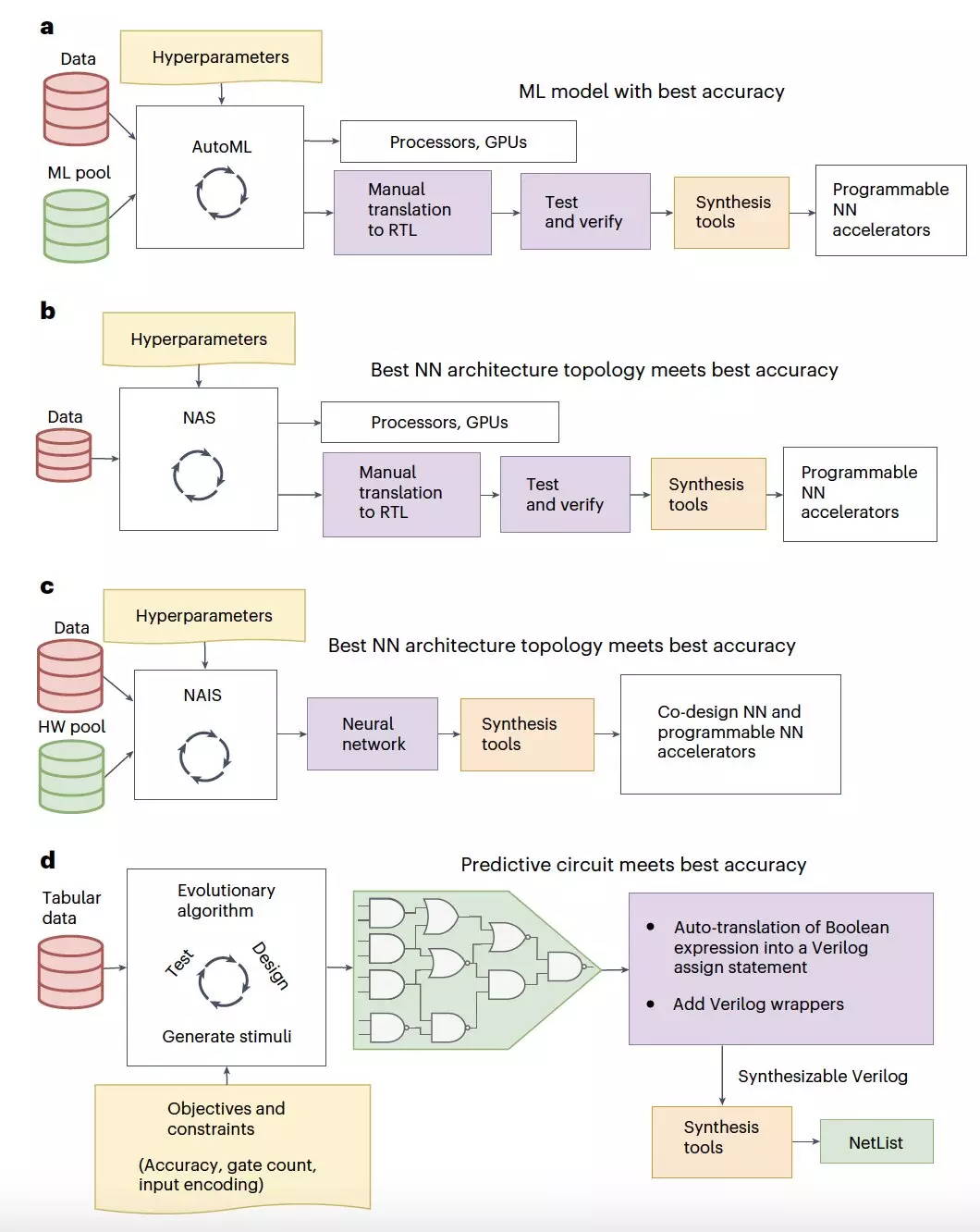
Deep learning techniques have made significant advancements in recent years, achieving human-level accuracy in various tasks such as image classification and natural language processing. The computational demands of these techniques have led to the development of hardware accelerators by researchers to efficiently run deep neural networks. One such innovative approach is the development of tiny classifiers, which are circuits consisting of a few hundred logic gates that can generate accurate predictions while using minimal hardware resources.
Researchers at the University of Manchester and Pragmatic Semiconductor have introduced a machine learning-based method to automatically generate classification circuits from tabular data, a combination of numerical and categorical information. The methodology proposed by the team, known as “tiny classifiers,” aims to maximize prediction accuracy while minimizing memory and area footprint for deployment on various computing devices.
The tiny classifier circuits developed by the researchers have shown promising results in terms of accuracy and power consumption. Despite their small size, these circuits achieve comparable prediction performance to conventional machine learning techniques. Utilizing an evolutionary algorithm, the researchers were able to automatically generate a classifier circuit with maximized training prediction accuracy, consisting of no more than 300 logic gates.
Through simulations, the researchers found that the tiny classifier circuits outperformed the best-performing machine learning baseline in terms of area and power consumption. Additionally, when implemented as a low-cost integrated circuit (IC), the tiny classifiers occupied significantly less space, consumed less power, and boasted better yield compared to existing ML baselines. This indicates the potential of tiny classifiers to be utilized in real-world applications.
The development of tiny classifiers opens up possibilities for efficiently addressing a wide range of real-world tasks. These circuits could be employed as triggering circuits on a chip for smart packaging and monitoring of goods, as well as in the creation of low-cost near-sensor computing systems. Their ability to deliver accurate predictions with minimal hardware resources makes them a promising solution for various applications in the field of deep learning.
The introduction of tiny classifiers represents a significant advancement in the field of deep learning. Their compact size, efficient performance, and potential for real-world applications make them a valuable asset in addressing various computational tasks. As researchers continue to explore and optimize the capabilities of tiny classifiers, they hold the promise of revolutionizing deep learning methodologies and contributing to advancements in artificial intelligence.
In the realm of software development, the ability to swiftly and accurately address bugs is…
The realm of quantum computing and communication is not just an abstract dream anymore; it…
In a remarkable leap for the field of material science, a collaborative research initiative has…
Throughout Earth's vast history, our planet has endured five major mass extinction events that reshaped…
Rainfall is a vital element of our planet’s hydrological cycle, yet many aspects of its…
On a night when the universe aligns, a mesmerizing phenomenon awaits: the appearance of the…
This website uses cookies.