
Urban areas play a significant role in shaping human health, environmental quality, and carbon footprint. A study conducted by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal) analyzed 919 European cities to identify different urban configurations and their impact on various factors. The findings of the research, published in The Lancet Planetary Health, shed light on the relationship between urban design and its implications for the well-being of residents.
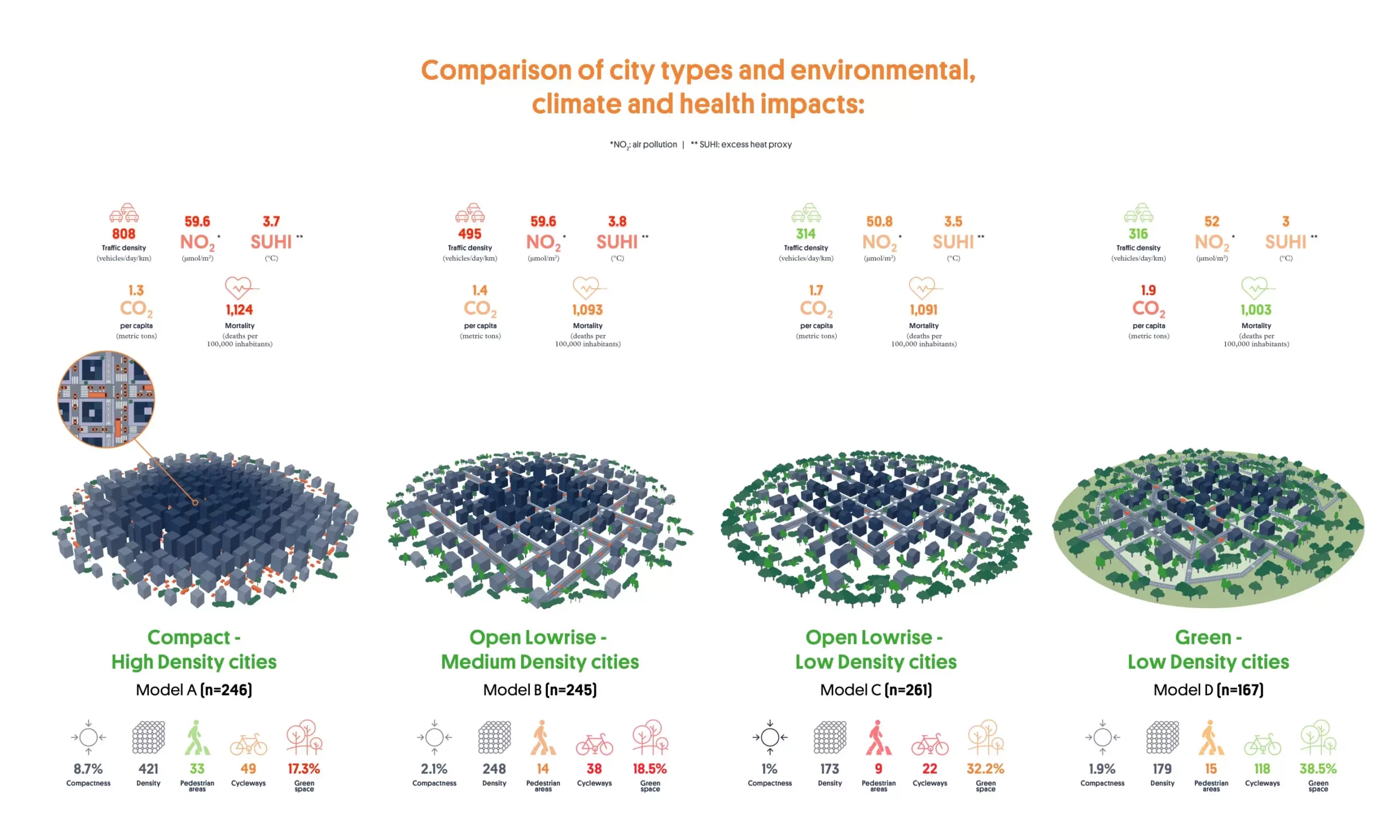
The study classified European cities into four basic urban configurations based on their design and population density. These configurations included compact-high density cities, open lowrise-medium density cities, open lowrise-low density cities, and green-low density cities. Each type of city had specific characteristics that influenced human health, environmental quality, and carbon footprint.
Compact-high density cities, such as Barcelona, Milan, Paris, and Basel, are characterized by small surface areas and high population densities. These cities tend to have limited green spaces, poor air quality, and a strong urban heat island effect. While they exhibit higher mortality rates and adverse exposure to air pollution, they have lower CO2 emissions per capita due to their energy-efficient infrastructure and compact layout.
Cities like Brussels, Dublin, and Leipzig fall under the category of open lowrise-medium density cities. These cities have medium population densities, relatively higher road densities, and moderate availability of pedestrian areas, cycleways, and green spaces. They offer a balance between compact-high density cities and open lowrise-low density cities in terms of urban design and environmental quality.
Open lowrise-low density cities, such as Pisa, Oviedo, and Toulouse, have larger surface areas and lower population densities compared to other city types. These cities lack pedestrian areas and cycleways but have moderate to high availability of green spaces on the outskirts. While they offer a more spacious living environment, they are less energy-efficient and require longer commutes.
Green-low density cities, including Helsinki, Rennes, Aarhus, and Stockholm, are characterized by large surface areas with low population densities. These cities prioritize green spaces, cycleways, and natural areas integrated throughout the urban landscape. While they have lower urban heat island effect and air pollution levels, they have higher carbon footprints per capita due to their sprawling nature and longer travel distances.
Compact-high density and open lowrise-medium density cities face significant challenges in terms of air pollution, urban heat island effect, and mortality rates. On the other hand, green-low density cities offer a healthier living environment but are less energy-efficient. The study highlights the need for innovative urban models, such as superblocks and nature-based solutions, to improve the environmental quality and sustainability of cities.
The impact of urban configuration on human health, environmental quality, and carbon footprint varies across different types of European cities. While compact cities have energy-efficient infrastructure but poor environmental quality, green cities offer a healthier living environment but higher carbon footprints. It is essential for cities to analyze their specific characteristics and design customized solutions to promote sustainability and well-being for their residents.
In the realm of software development, the ability to swiftly and accurately address bugs is…
The realm of quantum computing and communication is not just an abstract dream anymore; it…
In a remarkable leap for the field of material science, a collaborative research initiative has…
Throughout Earth's vast history, our planet has endured five major mass extinction events that reshaped…
Rainfall is a vital element of our planet’s hydrological cycle, yet many aspects of its…
On a night when the universe aligns, a mesmerizing phenomenon awaits: the appearance of the…
This website uses cookies.