
The clash between sustainable energy and traditional agriculture has become a pressing issue in today’s society. The Solé family in Alcarras de Carla Simón is a perfect example of this conflict, as their peach plantation faces challenges due to the installation of solar panels. This conflict highlights the urgent need for a solution that can balance the need for renewable energy with agricultural production. Cultural products and research are starting to reflect this tension, and the concept of agrivoltaics is emerging as a potential solution.
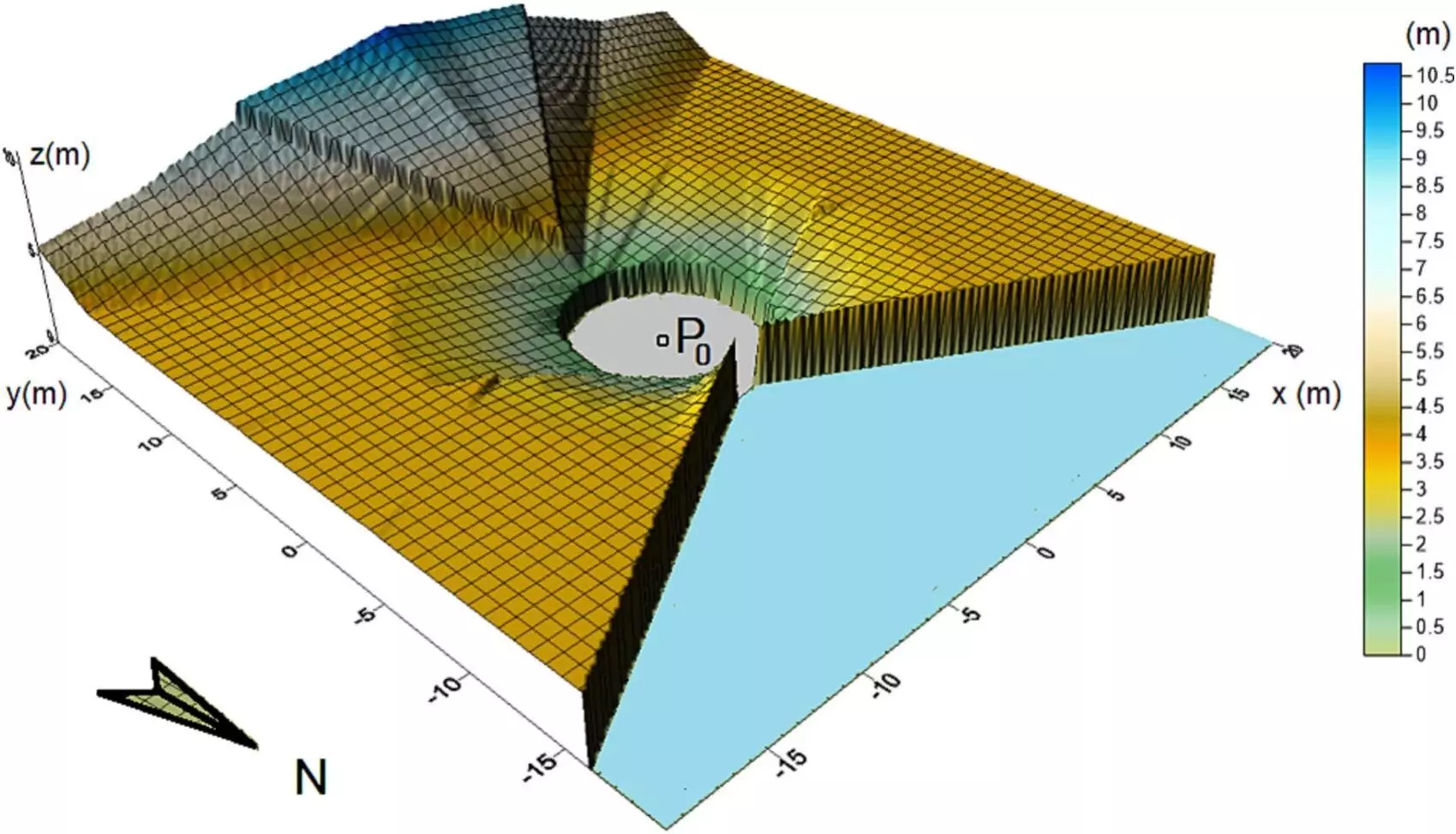
Agrivoltaics, which involves the co-use of land for agricultural and photovoltaic production, is gaining traction as a strategy to address the conflict between land use. To promote the implementation of agrivoltaic plants, the TEP215-Physics for Renewable Energies research group at the University of Cordoba has developed a new methodology. This approach focuses on defining the cultivable space between two-axis photovoltaic modules, allowing for the integration of crops within existing solar installations.
The research conducted by the team at the University of Cordoba is groundbreaking in its approach to agrivoltaics. By considering the theoretical simulation of solar astronomy and the spatial geometry of two-axis solar panels, the researchers were able to identify areas within the photovoltaic plant where crops could be grown without compromising solar panel movement or reducing energy production. This innovative methodology opens up new possibilities for the integration of agriculture and renewable energy production.
One of the key benefits of agrivoltaics is the symbiotic relationship between solar panels and crops. The shading provided by the panels can benefit the crops, particularly in extreme climates, by helping to maintain soil moisture. This mutual relationship enhances the sustainability of both agricultural and energy production. The implementation of agrivoltaics also contributes to the fight against climate change, making it a critical strategy for a more sustainable future.
The development of agrivoltaics represents a significant step towards the convergence of solar energy and agriculture. The findings of the research conducted by the University of Cordoba have paved the way for the conversion of existing large-scale photovoltaic plants into agrivoltaic systems. Moving forward, legislation on agrivoltaics and field trials with different crop types will be essential for the widespread implementation of this innovative land use strategy. By combining the benefits of solar energy and agriculture, agrivoltaics offers a promising solution to the challenges of sustainable land use in the face of climate change.
In the realm of software development, the ability to swiftly and accurately address bugs is…
The realm of quantum computing and communication is not just an abstract dream anymore; it…
In a remarkable leap for the field of material science, a collaborative research initiative has…
Throughout Earth's vast history, our planet has endured five major mass extinction events that reshaped…
Rainfall is a vital element of our planet’s hydrological cycle, yet many aspects of its…
On a night when the universe aligns, a mesmerizing phenomenon awaits: the appearance of the…
This website uses cookies.