
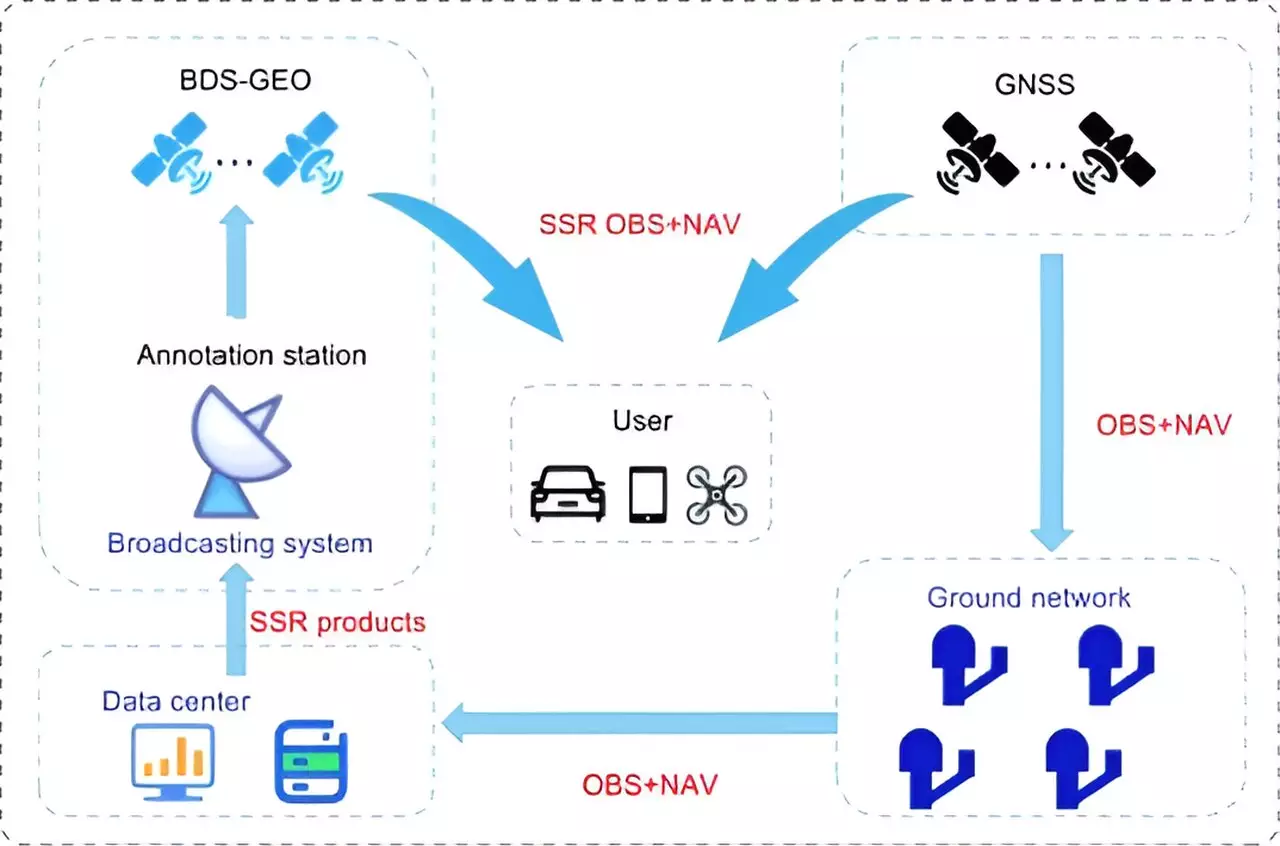
The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) is currently undergoing a significant upgrade to cater to the increasing need for high-precision positioning in various sectors. The new services being developed aim to provide decimeter-level accuracy within a matter of minutes, a substantial improvement over the existing capabilities. This upgrade is crucial for technologies like autonomous driving, robotic navigation, and smart city infrastructures, all of which rely heavily on precise location data for efficient operation.
Traditional systems such as the Global Positioning System (GPS), GLObal NAvigation Satellite System (GLONASS), and Galileo have already set high standards in the field, but they still face challenges like limited regional coverage and long convergence times. These challenges highlight the importance of improved navigation satellite systems, and the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) aims to address these issues by enhancing its high-precision services.
A recent study conducted by researchers from the Beijing Institute of Tracking and Telecommunication Technology, the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, and Wuhan University provides valuable insights into the high-precision services offered by the BeiDou system. Published in the journal Satellite Navigation on June 24, 2024, the study delves into the current state of the system, its achievements, and its future trajectory. The study specifically focuses on the PPP-B2b of BDS-3, which can achieve decimeter-level accuracy within 14 minutes. However, compared to international counterparts like Galileo’s High Accuracy Service (HAS) and Quasi-Zenith Satellite System’s (QZSS’s) Centimeter-Level Augmentation Service (CLAS), BDS-3 still faces challenges in terms of regional coverage and convergence time.
To overcome these limitations, the research proposes a multi-layer development framework that emphasizes the integration of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites. By incorporating a constellation of 288 LEO satellites, the positioning accuracy of the system can be improved to better than 5 cm within approximately 1 minute. This enhancement not only enhances global coverage but also significantly reduces convergence time, making the BeiDou system a strong contender in the high-precision satellite navigation arena.
Dr. Xingxing Li from Wuhan University highlighted the significance of the advancements in BeiDou’s high-precision services in meeting the escalating demands of modern navigation applications. The integration of LEO satellites shows particular promise in enhancing coverage and reducing convergence time, bringing the system closer to achieving real-time, centimeter-level positioning accuracy on a global scale. This progress opens up new possibilities for applications like autonomous driving, unmanned aerial vehicles, and smart device navigation, signaling a major evolution in global navigation satellite systems and solidifying BeiDou’s position as a leader in high-precision services.
Despite the term "rare," rare earth metals (REMs) are not nearly as scarce as their…
A collaboration led by Rutgers University-New Brunswick has initiated a paradigm shift in our understanding…
Natural gas leaks are a growing concern in both urban and rural settings, with potential…
Recent groundbreaking research at the University of Vienna has unveiled a novel interplay of forces…
In recent years, perovskites have garnered significant attention in the fields of materials science and…
For decades, astronomers have probed the depths of the Milky Way, grappling with two perplexing…
This website uses cookies.