
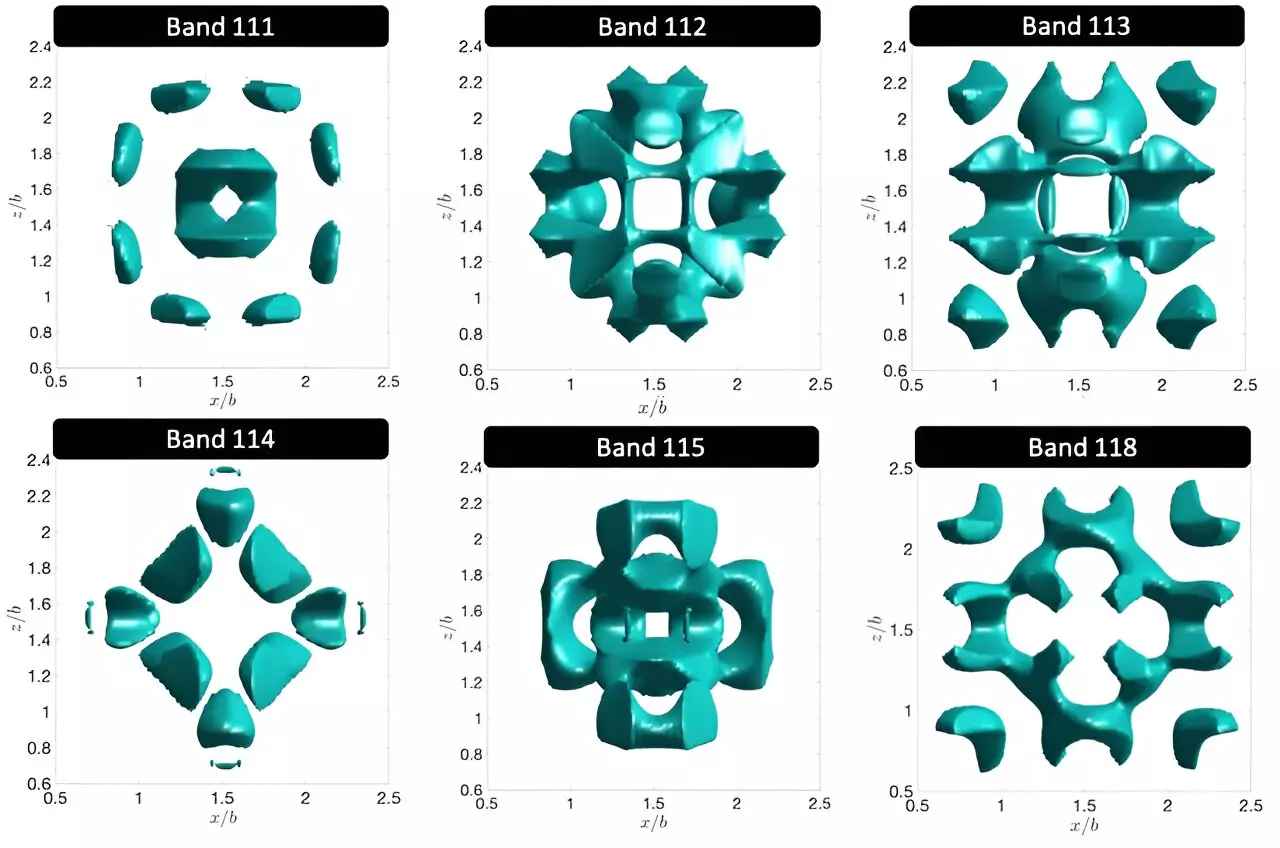
Researchers at the University of Twente have recently delved into the world of photons, shedding light on the fascinating behavior of these elementary particles that make up light. Unlike electrons, which are confined by atomic nuclei in specific orbitals, photons have the freedom to roam with an incredible variety of shapes and symmetries. This newfound understanding of photonic orbitals opens up a realm of possibilities in various fields, from smart LED lighting to quantum computing.
Through a computational study, the researchers focused on how photons interact within a 3D nanostructure known as a photonic crystal. By strategically designing these structures to contain defects, they were able to create an environment that isolates and controls photonic states. This approach, made possible by nanotechnology, offers a level of flexibility and precision that is unparalleled in the realm of electronic orbitals and chemistry.
The implications of these findings extend far beyond theoretical physics. Photonic orbitals play a critical role in the development of cutting-edge optical technologies, including quantum computing and high-sensitivity photonic sensors. By manipulating the structure of nanostructures, researchers can enhance the local density of optical states, paving the way for advancements in cavity quantum electrodynamics and the integration of quantum dots.
The potential applications of photonic orbitals are vast and diverse. From revolutionizing the efficiency of lighting systems to enabling the creation of networks of single photons, the impact of this research is poised to reshape the technological landscape. By harnessing the unique properties of photons and leveraging the capabilities of nanotechnology, researchers are unlocking new possibilities for innovation in the field of photonics.
The study conducted by the University of Twente researchers has provided invaluable insights into the behavior and control of photons in structured environments. By exploring the complex world of photonic orbitals, they have laid the groundwork for future advancements in optical technologies, quantum computing, and beyond. As we continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with light, the potential for transformative discoveries in this field is truly limitless.
In the realm of software development, the ability to swiftly and accurately address bugs is…
The realm of quantum computing and communication is not just an abstract dream anymore; it…
In a remarkable leap for the field of material science, a collaborative research initiative has…
Throughout Earth's vast history, our planet has endured five major mass extinction events that reshaped…
Rainfall is a vital element of our planet’s hydrological cycle, yet many aspects of its…
On a night when the universe aligns, a mesmerizing phenomenon awaits: the appearance of the…
This website uses cookies.