
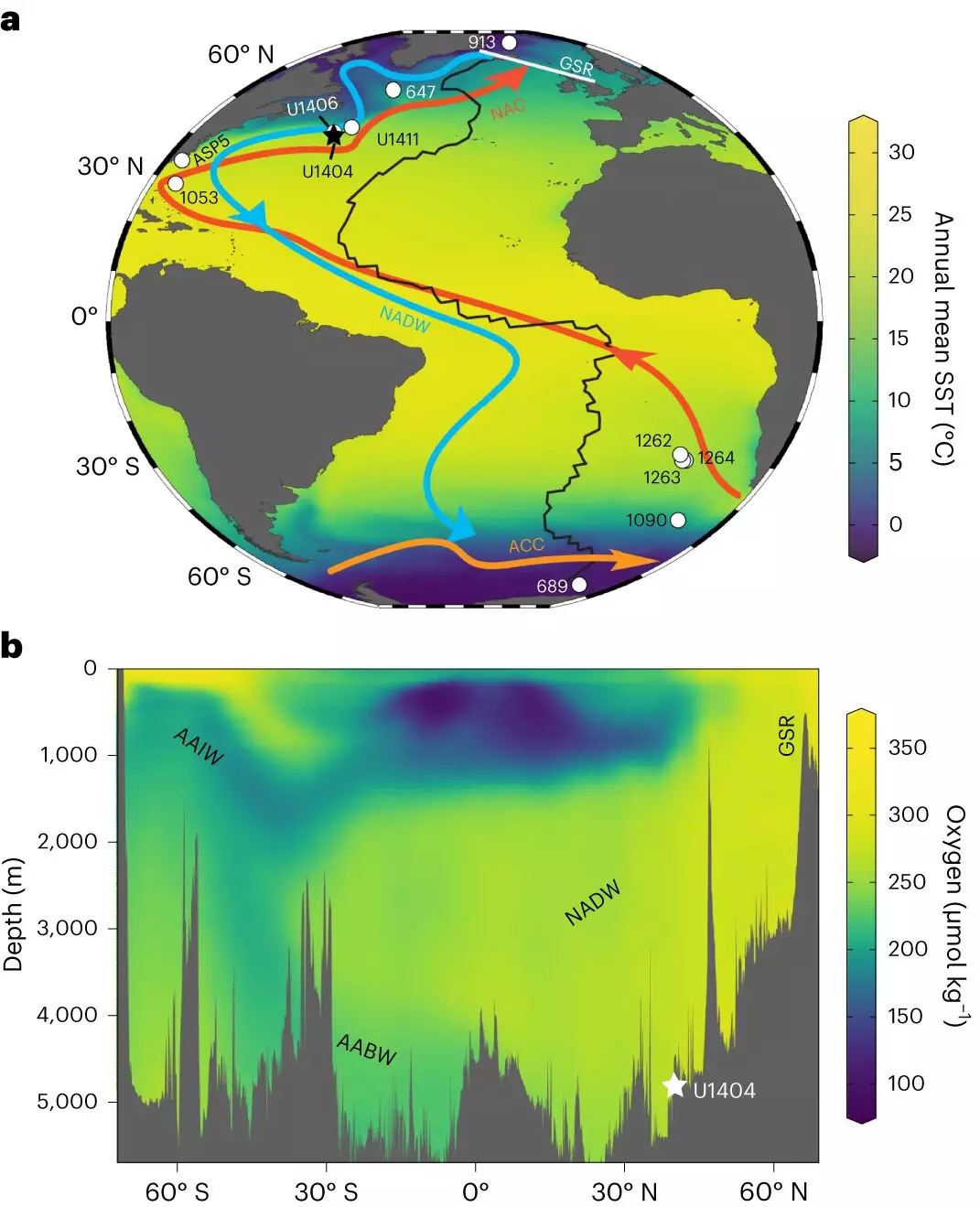
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) plays a crucial role in global climate and marine ecosystems, with its ability to redistribute heat and salt in the ocean, interact with the atmosphere, and ventilate the ocean interior. Despite its significance, the timing and cause of the inception of AMOC and its subsequent evolution have remained unclear. However, a recent study published in Nature Geoscience by researchers from the Institute of Earth Environment of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IEECAS), the University of Hong Kong, and the University of Southampton sheds new light on this topic.
In their groundbreaking research, the team proposed a novel method for tracing oxygenation using microbial biomarkers. By analyzing distributions of glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers (GDGTs), the researchers were able to identify microbial source indicators that indicate the contribution of other archaea/bacteria relative to the ubiquitous marine Thaumarchaeota. This approach provided valuable insights into the oxygenation status of past oceanic environments.
Through their investigation, the researchers discovered that the evolution of early AMOC was closely linked to changes in oxygenation. The oxygenation of AMOC-feed waters decreased and reached its lowest point towards the end of the Eocene period. However, with the initiation of large-scale Antarctic glaciation around 34 million years ago (Ma), the AMOC-feed waters became better oxygenated. This marked the onset of a more modern-like AMOC at the Eocene-Oligocene transition (EOT). The study suggests that the initiation of Antarctic glaciation was a key trigger for the onset of the modern-like AMOC.
In understanding the mechanisms driving the Cenozoic AMOC, the researchers emphasized the importance of both vertical mixing and Southern Ocean wind-driven upwelling. These factors are essential for sustaining the modern AMOC system. The study highlights the complex interplay of various oceanic processes in the evolution and maintenance of AMOC.
The findings of this study provide significant insights into the timing and cause of the inception of AMOC. Understanding the evolution of this system is crucial for predicting future climate scenarios and their potential impacts on marine ecosystems. Future research should focus on further investigating the role of Antarctic glaciation and other key drivers in the development and stability of AMOC.
The research conducted by the IEECAS, the University of Hong Kong, and the University of Southampton sheds new light on the evolution of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation. By utilizing microbial biomarkers and tracing oxygenation, the researchers were able to uncover the role of Antarctic glaciation as a trigger for the onset of a more modern-like AMOC. Furthermore, they emphasized the importance of vertical mixing and Southern Ocean upwelling in sustaining the AMOC system. This study contributes valuable knowledge to our understanding of the mechanisms driving AMOC and its significance in global climate and marine ecosystems. Continued research in this field will undoubtedly enhance our ability to comprehend and predict the future behavior of this critical oceanic circulation system.
In the realm of software development, the ability to swiftly and accurately address bugs is…
The realm of quantum computing and communication is not just an abstract dream anymore; it…
In a remarkable leap for the field of material science, a collaborative research initiative has…
Throughout Earth's vast history, our planet has endured five major mass extinction events that reshaped…
Rainfall is a vital element of our planet’s hydrological cycle, yet many aspects of its…
On a night when the universe aligns, a mesmerizing phenomenon awaits: the appearance of the…
This website uses cookies.