
A recent study published in the prestigious journal Science has revealed a groundbreaking development by a team of chemists and materials scientists at Sichuan University in China. The researchers have successfully created a photoluminescent aerogel with a remarkable visible light reflectance of 104%.
With the global climate crisis worsening, there is a growing demand for innovative solutions to help people stay cool. One promising avenue of research is the development of passive radiative cooling materials. Unlike traditional cooling methods, these materials provide cooling capabilities inherently rather than through an energy-consuming process.
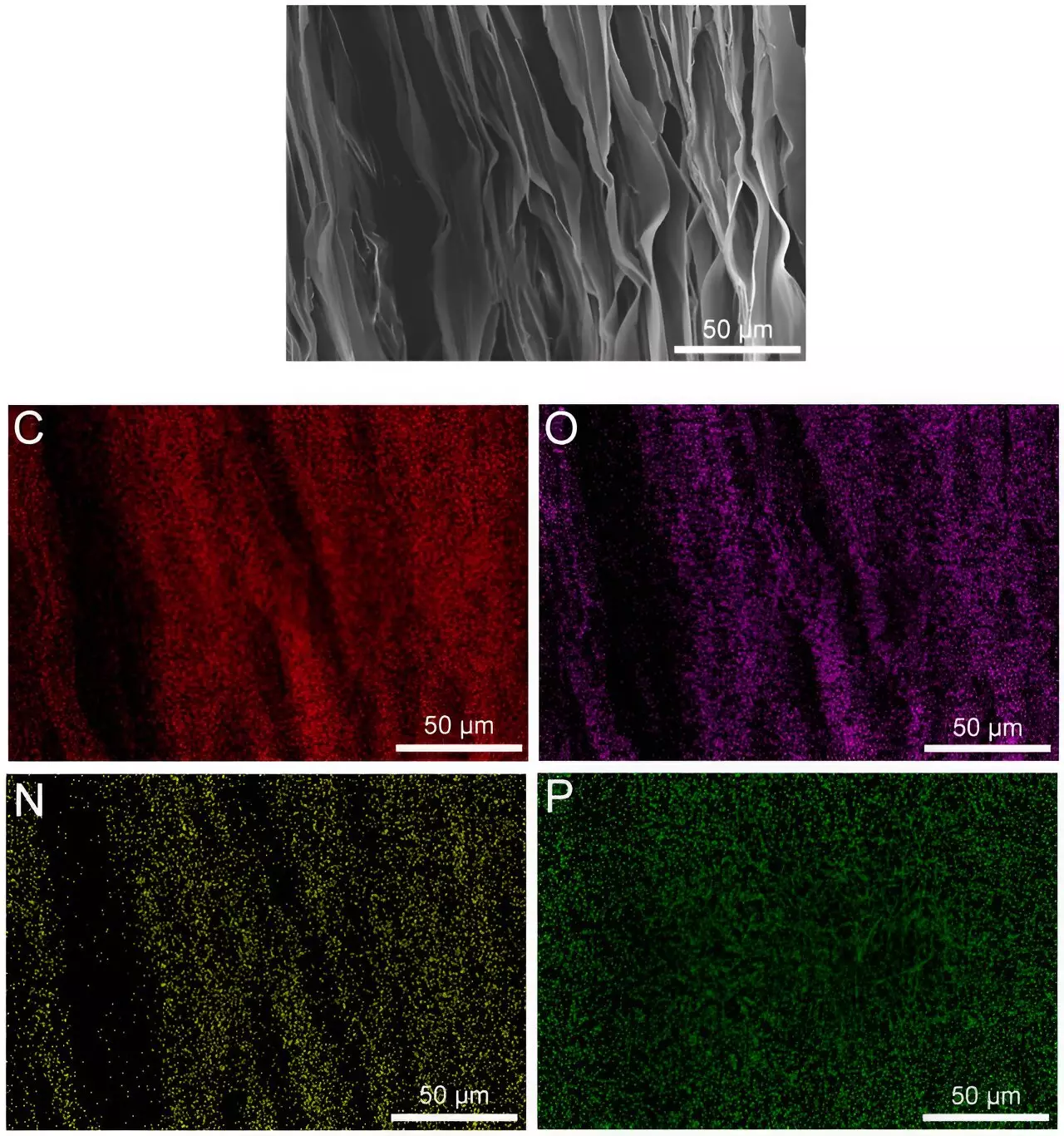
The team of researchers in China utilized readily available biomass to create their photoluminescent aerogel. By incorporating freeze-dried salmon sperm DNA into a gelatin sample, they were able to produce a highly compressed layered aerogel with remarkable light reflectance properties. The material’s photoluminescence allows it to reflect more light than it receives, making it an ideal candidate for passive cooling applications.
The photoluminescent aerogel developed by the Chinese researchers demonstrates self-healing capacity when damaged, thanks to its ability to absorb water. This environmentally friendly material is held together by hydrogen bonds between phosphates in the DNA and amino acids in the gelatin. Moreover, tests have shown that it is capable of reflecting an astounding 104% of the light that strikes it, effectively cooling the surface of a structure to 16°C below ambient temperature.
The development of this photoluminescent aerogel opens up new possibilities for sustainable cooling solutions in various applications. From residential buildings to industrial facilities, the use of passive radiative cooling materials could significantly reduce energy consumption and contribute to mitigating the impact of climate change. Researchers worldwide are now exploring ways to further enhance the performance and versatility of such materials for widespread implementation.
The pioneering work of the Chinese research team represents a major step forward in the field of materials science and sustainable technology. The photoluminescent aerogel they have developed holds tremendous potential for revolutionizing cooling systems and reducing carbon emissions associated with traditional cooling methods. As the global community continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, innovative solutions like this aerogel offer hope for a more sustainable future.
A groundbreaking expedition led by an international research team, featuring esteemed scientists from the University…
The pursuit of coherent control over wave transport and localization stands as a monumental challenge…
In recent astronomical explorations, researchers have unearthed a striking phenomenon emanating from a distant corner…
The quest for sustainable practices within the chemical industry is more critical than ever. Researchers…
In the complex interplay of human health, the relationship between the gut and the brain…
The relentless drive for sustainable energy solutions has fueled remarkable advancements in solar technology, with…
This website uses cookies.