
Researchers at Oregon State University and Baylor University have discovered a groundbreaking technique to lower the energy consumption of photonic chips utilized in data centers and supercomputers. The study has been published in the Scientific Reports journal. Data centers can consume up to 50 times more energy per square foot of floor space than a regular office building, as per the US Department of Energy. Data centers store, process, and disseminate data and applications, and account for around 2% of all electricity usage in the United States, according to the DOE. The number of data centers has increased substantially as the demand for data has risen, as per the US International Trade Commission. In the US, companies including Facebook, Amazon, Microsoft, and Google, which produce and consume huge quantities of data, have more than 2,600 data centers.
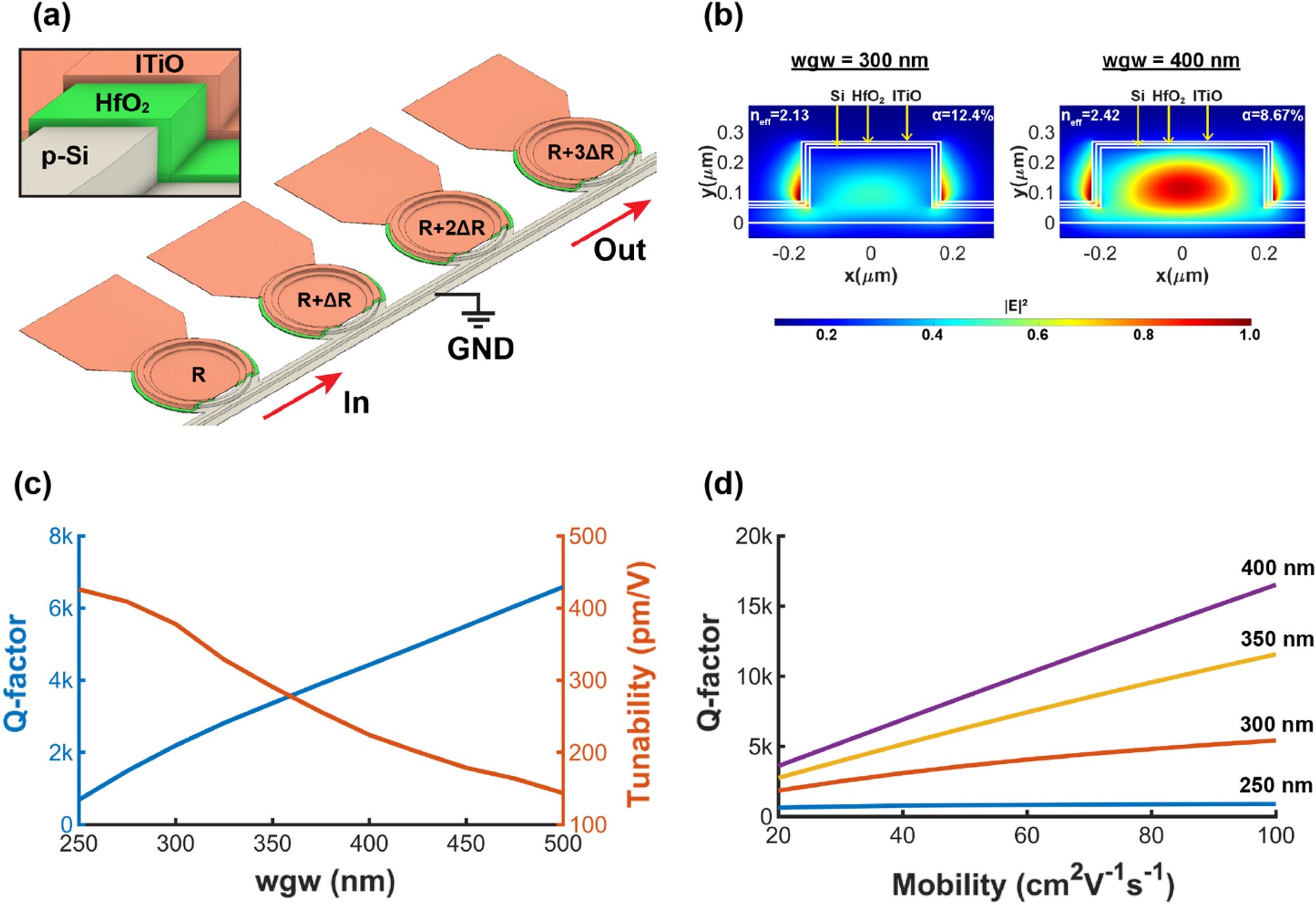
The team, which includes John Conley of the OSU College of Engineering, former Oregon State colleague Alan Wang, now of Baylor, and OSU graduate students Wei-Che Hsu, Ben Kupp, and Nabila Nujhat, has created an innovative and ultra-energy efficient method to counterbalance temperature variations that deteriorate photonic chips. Photonic chips use photons instead of the electrons used in traditional computer chips to transmit data at the speed of light, allowing for extremely quick and energy-efficient data transmission. The problem with photonic chips is that, until now, maintaining their temperature stability and performance required a significant amount of energy. However, Wang’s team has discovered that the energy required for temperature control may be reduced by a factor of more than one million.
The photonics industry solely relies on “thermal heaters” to fine-tune the working wavelengths of high-speed, electro-optic devices to optimize their performance, according to Wang. These thermal heaters consume several milliwatts of electricity per device. However, when multiplied by millions of devices, these milliwatts add up quickly, posing problems as systems scale up and become more massive and more potent. The team’s method uses gate voltage to control temperature, requiring virtually no electric current.
Conley stated that the team’s approach is much more sustainable and will enable data centers to become faster and more potent while utilizing less energy, allowing for more powerful applications driven by machine learning, such as ChatGPT, to be accessed without guilt. The team’s breakthrough in reducing energy consumption in photonic chips is significant in light of the rising number of data centers globally. The need for energy-efficient solutions to maintain the growth of data centers and supercomputers is critical, and the team’s innovative solution is a step in the right direction.
In the realm of software development, the ability to swiftly and accurately address bugs is…
The realm of quantum computing and communication is not just an abstract dream anymore; it…
In a remarkable leap for the field of material science, a collaborative research initiative has…
Throughout Earth's vast history, our planet has endured five major mass extinction events that reshaped…
Rainfall is a vital element of our planet’s hydrological cycle, yet many aspects of its…
On a night when the universe aligns, a mesmerizing phenomenon awaits: the appearance of the…
This website uses cookies.