
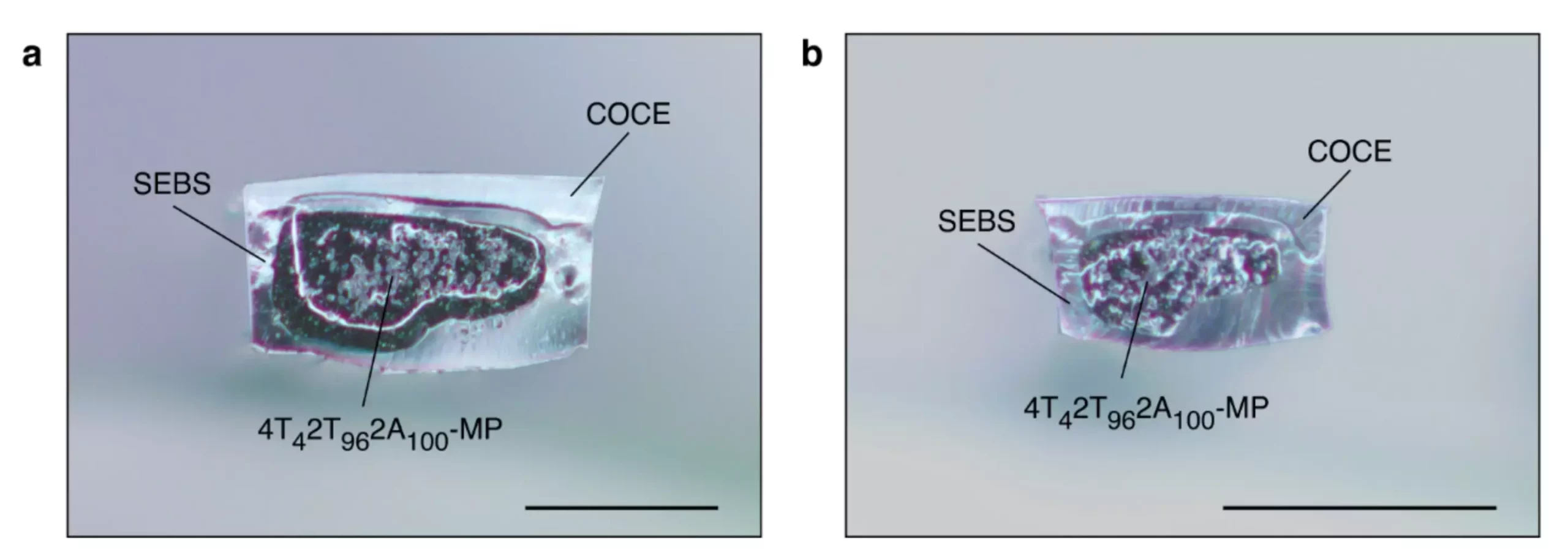
A research team at MIT has developed a new method of creating magnetic soft robots that provides locomotion under unidirectional magnetic fields. The team combined fiber-based fabrication systems with mechanical and magnetic programming methods to create 3D soft robots that can be controlled using magnets. The development of these robots is an important advancement in the field of soft robotics, as previous efforts to create magnetically controlled soft robots have been plagued by problems with deployment, scaling and production.
The team at MIT overcame the challenges presented by magnetically controlled soft robots by using fiber-based actuators and magnetic elastomer composites. The actuators were created using thermal drawing, which allowed for the creation of a stretchy ferromagnetic compound. Each of the structures were then subjected to a strain regimen that forced them into a helical structure. These structures allowed for folding on-demand via magnetic pull at multiple points, in a way that led to constriction and relaxation, similar to the way caterpillars move. Adding folding points allowed for greater flexibility. To mimic bipedal motion, folding points were introduced that forced sectioned structures into linear leg and foot shapes.
One of the main challenges to using magnets to control soft robots is the bulkiness of the equipment that is needed. The research team overcame this problem by using fiber-based actuators and magnetic elastomer composites. The resulting 3D robots could be controlled by varying the strain applied to a given robot and the strength of a magnetic field. The result was worm-like robots, some that crawled and some that walked. The researchers note that locomotion was induced using a magnetic field placed orthogonally to the plane of motion.
The robots are designed to be scalable and can be programmed to carry cargo or to perform in unison with other similar robots. The robots are controlled by varying strain and magnetic field strength. The researchers point out that the design of the robots paves the way for their use in both biomedical and engineering applications.
The development of magnetic soft robots is an important advancement in the field of soft robotics. The research team at MIT has overcome the challenges presented by magnetically controlled soft robots by using fiber-based fabrication systems with mechanical and magnetic programming methods. The resulting 3D robots can be controlled using magnets and can be programmed to carry cargo or to perform in unison with other similar robots. The design of the robots is scalable and paves the way for their use in both biomedical and engineering applications.
The battle against antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has become one of the paramount public health challenges…
In our relentless pursuit of healthier lifestyles, the craze for sugar alternatives has become a…
As climate change continues to wreak havoc globally, Africa's vulnerability makes it imperative for nations…
The realm of quantum technology has long been hailed as the next frontier in scientific…
The fascination surrounding black holes often breeds misconceptions, particularly the idea that they obliterate not…
In a groundbreaking endeavor, researchers at Trinity College Dublin have merged the worlds of chemistry…
This website uses cookies.