
Building design methods have traditionally focused on improving the connectivity between structural components to ensure that loads are redistributed in the event of component failure. However, while these methods are effective in addressing small initial failures, they can increase the risk of progressive collapse after large initial failures, potentially leading to complete or large-scale collapses. Recent incidents such as the collapse of Champlain Towers, a building in Peñíscola, and a building in the Iranian city of Abadan have highlighted the need for a new approach to building design to prevent catastrophic collapses.
A groundbreaking design method proposed by researchers from ICITECH-UPV is set to revolutionize the way buildings are constructed. This new approach, published in the journal Nature, introduces the concept of fuse-based segmentation to prevent the propagation of major failures throughout a building in the event of an initial failure. By isolating damaged parts of the structure, this innovative method aims to safeguard the rest of the building and minimize the extent of damages.
The principle behind the fuse-based segmentation method is akin to protecting an electrical system with fuses against overloads. By incorporating structural fuses into the building design, the structure maintains continuity under normal conditions but can be segmented when failure propagation becomes inevitable. According to co-author Nirvan Makoond, this approach effectively reduces the risk of total collapse and prevents catastrophic outcomes.
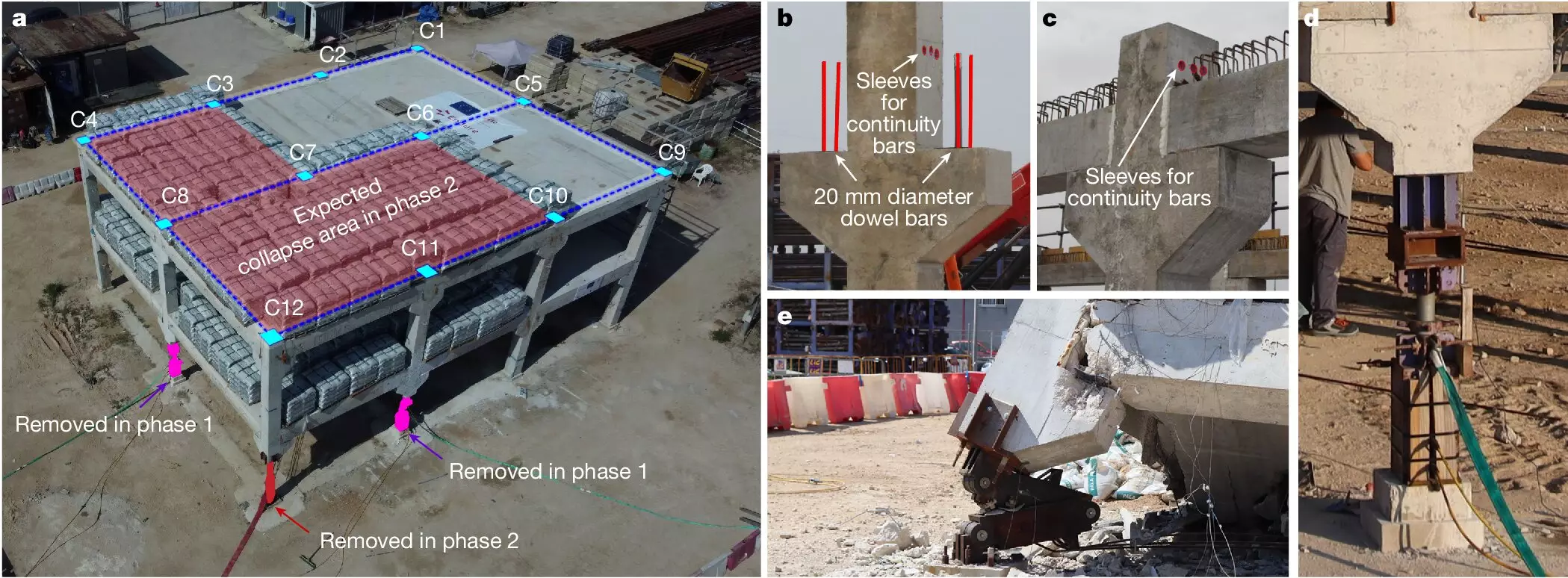
One of the key advantages of this new design method is its minimal impact on the cost of construction. By utilizing conventional construction details and materials, the implementation of fuse-based segmentation can be seamlessly integrated into the design of new buildings. The researchers have successfully validated the method through tests on a real-scale building made of prefabricated concrete, demonstrating its effectiveness in preventing collapse propagation.
As the research team continues to refine and expand the methodology, the applicability of fuse-based segmentation is expected to extend to buildings constructed with in-situ concrete and steel. The ongoing development of this innovative design approach marks a significant milestone in the field of building construction, offering a promising solution to mitigate the risk of catastrophic collapses. The success of the method was further underscored by a world-first test conducted in June 2023 as part of the Endure project.
The fuse-based segmentation approach represents a paradigm shift in building design, prioritizing resilience and safety in the face of potential structural failures. With its proven efficacy and minimal cost impact, this innovative method has the potential to revolutionize the way buildings are constructed and safeguard human lives. The collaborative efforts of the research team from ICITECH-UPV have yielded a groundbreaking solution that promises to shape the future of structural engineering.
In the realm of software development, the ability to swiftly and accurately address bugs is…
The realm of quantum computing and communication is not just an abstract dream anymore; it…
In a remarkable leap for the field of material science, a collaborative research initiative has…
Throughout Earth's vast history, our planet has endured five major mass extinction events that reshaped…
Rainfall is a vital element of our planet’s hydrological cycle, yet many aspects of its…
On a night when the universe aligns, a mesmerizing phenomenon awaits: the appearance of the…
This website uses cookies.